CATEGORY
Repacking Services England and Germany
The report covers the list of leading repackers or contract packagers in England and Germany, types of services offered by them and the best enagement practices in this industry
Beroe LiVE.Ai™
AI-powered self-service platform for all your sourcing decision needs across 1,200+ categories like Repacking Services England and Germany.
Market Data, Sourcing & Supplier Intelligence, and Price & Cost Benchmarking.
Schedule a DemoThe World’s first Digital Market Analyst
Abi, the AI-powered digital assistant brings together data, insights, and intelligence for faster answers to sourcing questions
Abi is now supercharged with GPT4 AI engine. Enjoy the ease of ChatGPT, now on Abi
Repacking Services England and Germany Suppliers
Find the right-fit repacking services england and germany supplier for your specific business needs and filter by location, industry, category, revenue, certifications, and more on Beroe LiVE.Ai™.
Schedule a Demo


Use the Repacking Services England and Germany market, supplier and price information for category strategy creation and Quaterly Business Reviews (QRBs)
Schedule a DemoRepacking Services England and Germany market report transcript
Regional Market Outlook on Repacking Services
Europe is expected to witness a growth rate of 8–9 percent between 2018 and 2022. Rising demand from end-use segments, like food & beverage, pharmaceutical & automotive is a major driver for co-packaging services in Europe.
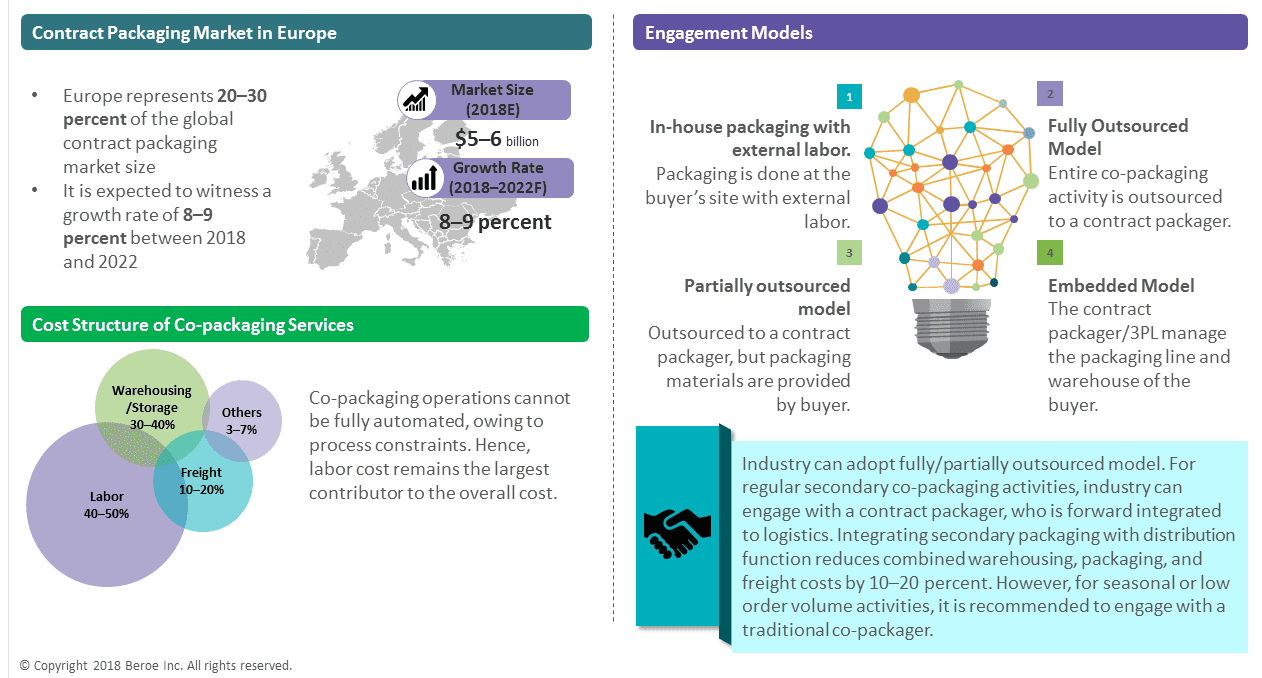
Engagement Models
In-House Packaging With External Labor
Hiring seasonal/temporary labors for packaging activities at the buyers' site. Though not a preferred practice, some buyers use it for lower order volume destined for shorter distance deliveries.
When is it used?
In cases of low order volume packaging, which involves delivery to few locations, external labor can be hired for packaging in-house. In cases of seasonal promotional activities for a specific region alone, this model can be used.
Pros
- Inventory control
- Control over the packaging
- Brand loyalty: look and feel of the product is completely in buyers control
Cons
- Prone to price fluctuations from the labor market
- Preliminary training must be provided to the labor
Fully Outsourced Model
The co-packaging activity is entirely outsourced to a contract packager. Contract packagers are nowadays forward integrated towards logistics and distribution.
When is it used?
- Mature product in an established market
- Order volume is large
- Involves more shipping locations
Pros
- Reduced burden of rent and labor
- Access to logistics services
- bsorb cost spikes
- Free pick-and-pack solutions
- Additional value-added service
Cons
- Lack of control
- No accurate inventory
- Hidden fees and additional charges
Embedded Model
The co-packager installs packaging line at the buyers' site or the buyer leases their entire warehouse to a co-packager who manages the end-to-end function from sourcing of materials to distribution of products.
When is it used?
- Buyer has sufficient warehouses to cater to the needs of the market
- en order volume is large, and continuous operation is expected
Pros
- Inventory control
- Reduced burden of rent and labor
- Access to logistics services
- Absorb cost spikes
- Additional value-added service
Cons
- Hidden fees and additional charges
- Contracts matter a lot in embedded model
- Certain suppliers do not involve in this practice unless the scope of profit is higher or in some cases, the warehouse is shared warehouse where the supplier can cater to different clients under one roof
Partially Outsourced Model
The co-packaging activity is entirely outsourced, except sourcing of packaging materials, which the buyers provides to the contract packager.
When is it used?
- Buyer has some patented packaging designs
- Buyers have the ability to exercise control over packaging material by sourcing it themselves
- Co-packager packaging materials does not meet buyer standards
Pros
- Brand loyalty: Look and feel of the product is completely in buyers' control
- Reduced burden of rent and labor
- Access to logistics services
- Absorb cost spikes
- Free pick-and-pack solutions
- Additional value-added service
Cons
- Largely depended on packaging material delivery to the supplier, any delay would cause delay in the entire system
- No accurate inventory
- Hidden fees and additional charges
Cost Structure: Co-Packaging Services
Labor constitutes a major portion of co-packaging cost. Any change in the labor market will have a direct impact on the cost of co-packaging services. The need to reduce dependency on labor is a major reason for increasing demand and investments for new automations in co-packaging.
Labor
Labor cost is one of the major drivers that impacts the average package cost, as labor costs contribute substantially to the overall cost, the average package cost might increase if the service provider does not use technology optimally to reduce labor costs.
Warehousing
Warehousing/storage costs form the second largest component of the co-packaging service costs. The share of warehousing/storage costs while engaging with a traditional co-packager might be low compared to a large integrated player/3PL, owing to relatively higher market power that the integrated players hold
Packaging materials
Packaging materials are either sourced by the co-packager or the buyer provides the packaging materials. Any fluctuations in the raw material prices of packaging materials may induce price variations in the overall packaging cost
Interesting Reads:
Discover the world of market intelligence and how it can elevate your business strategies.
Learn more about how market intelligence can enable informed decision-making, help identify growth opportunities, manage risks, and shape your business's strategic direction.
Get Ahead with AI-Enabled Market Insights Schedule a Demo Now
