CATEGORY
Warehouse Automation System Europe
Beroe LiVE.Ai™
AI-powered self-service platform for all your sourcing decision needs across 1,200+ categories like Warehouse Automation System Europe.
Market Data, Sourcing & Supplier Intelligence, and Price & Cost Benchmarking.
Schedule a DemoThe World’s first Digital Market Analyst
Abi, the AI-powered digital assistant brings together data, insights, and intelligence for faster answers to sourcing questions
Abi is now supercharged with GPT4 AI engine. Enjoy the ease of ChatGPT, now on Abi
Warehouse Automation System Europe Suppliers
Find the right-fit warehouse automation system europe supplier for your specific business needs and filter by location, industry, category, revenue, certifications, and more on Beroe LiVE.Ai™.
Schedule a Demo


Use the Warehouse Automation System Europe market, supplier and price information for category strategy creation and Quaterly Business Reviews (QRBs)
Schedule a DemoWarehouse Automation System Europe market report transcript
Regional Market Outlook on Warehouse Automation System
Client can benefit from quick ROI by implementing warehouse automation since most of their facilities are located in Western European countries
Warehouse Automation is turned out be more of a necessity than an option in Western Europe and North America where rental rates and labor wages are high and availability of skilled labors are low, which directly influences the warehousing operating cost
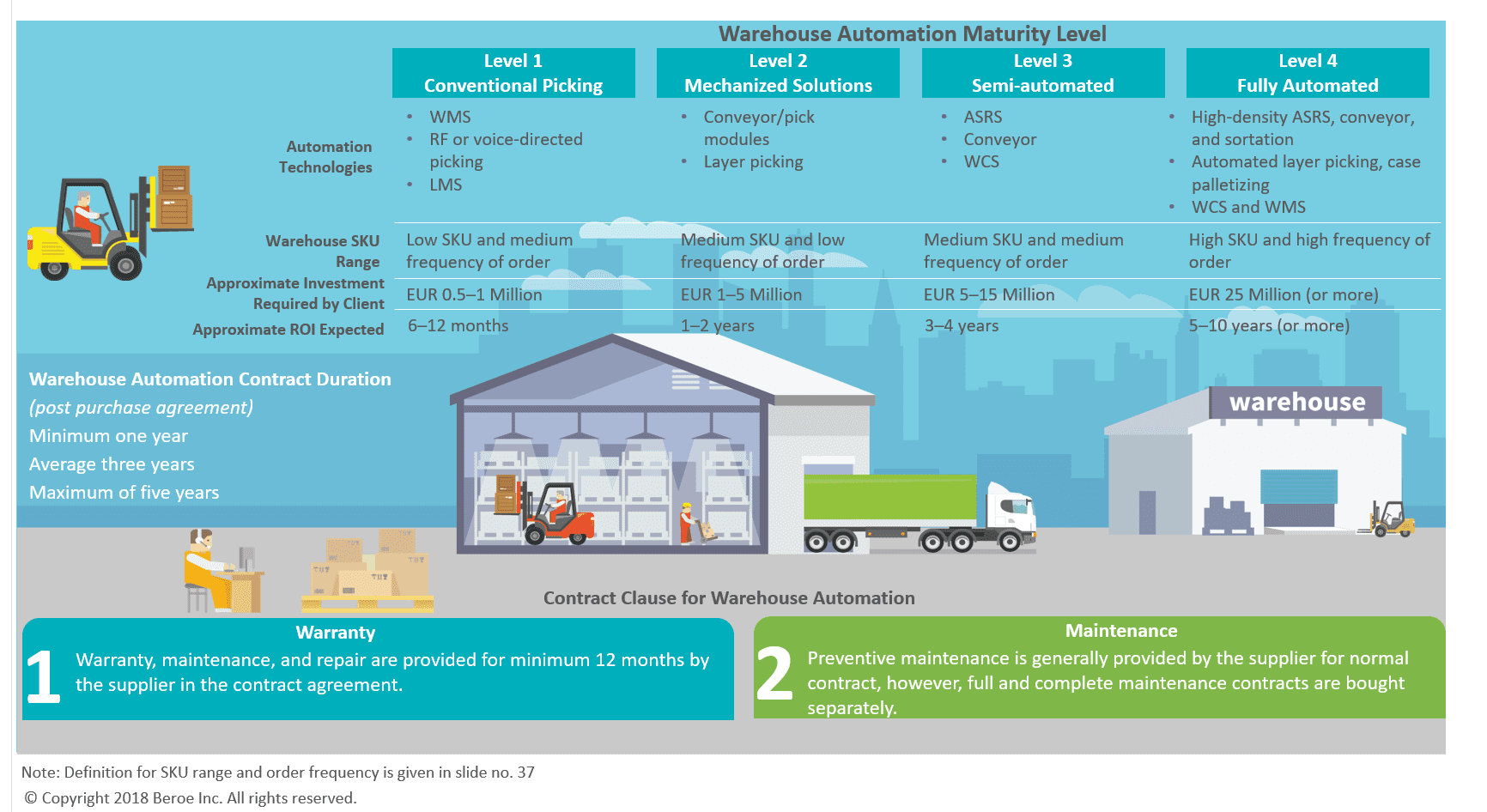
Major Factors Influencing Automation ROI
- Labor Costs–higher savings in high-cost labor markets
- Real Estate Costs–high cost areas can better justify by increasing vertical utilisation rather than expansion
- Volume: Number of cases or pallets handled daily, both inbound and outbound
- Order Complexity: Outbound order profiles, such as individual parcels, mixed SKU pallets, or store-friendly sequencing
Benefits of Warehouse Automation
- AS/RS with warehouse material handling systems drastically simplifies the picking process to improve order fulfillment
- Reduced fixed costs through optimized land use and equipment
- Reduction in variable costs due to less labor and increase in operation efficiency without compromising quality and service level of the product
- Higher productivity even in sub-zero conditions
AGVs
AGV is highly used in warehouse linked to manufacturing plants compared to dedicated distribution warehouse, primarily used for intra-facility transportation/shuttling of palletized goods, this is due to very static and repetitive movement paths in manufacturing.
- The manufacturing sector is the primary end user, accounting for ~75 percent, while the remaining is for distribution centers/warehouses
- Approximately, 70 percent of the AGV installations go into existing facilities, while the rest is from new warehouse, this reflects the trend of AGV being used to reduce the labor cost in manufacturing and warehousing environment
- In a conventional forklift environment, used for handling, driver is the most expensive cost in vehicle operation
- E.g., in a seven day, 24-hour operation, the driver cost constitutes to 80–90% of the per vehicle operating cost, which is ~EUR200,000
Types of AGVs
Masted Vehicles
- Forked and clamped vehicles are the masted vehicles
- This is a most flexible type of vehicle and has the ability to interface with the floor, racks, and conveyors
- This resembles more like a manual lift truck models
Unit Loads
- These vehicles have a compact design, with vehicle directly under the load
- These have the ability to interface with the stands and the conveyors
- They do not have the load handling ability unless loaded/unloaded by external means
Tows or Tuggers
- These vehicles, typically, carry up to three-wheeled carts
- Loads will have to be placed manually on the vehicle
- It is considered as the most economical solution compared to other types, when one load is carried per trip
Carts and Custom Vehicles
- Carts, typically, operate lighter loads, which is less than 2,000 lb., very simple, no traffic control and is considered as the simplest type of load handling vehicle
- Custom vehicles are designed to move unique loads, based on the size, shape, and capacity
Major Navigating Methods of AGVs
Laser Navigation Systems
- Most popular and widely used method of navigation systems
- Reflective targets are mounted throughout the facility at the required positions
- Laser scanner, which is on the top of the vehicle strobes for the reflective targets
- The vehicle control algorithm calculates the exact vehicle position via triangulation
Magnetic Tape Navigation Systems
- The magnetic tapes are adhered on the surface of the floor
- The sensor on the underside of the vehicle detects the magnetic tape
- The vehicle operates off tape via dead recoknoning and is much similar to wire-guided navigation systems
Wire Navigation Systems
- The vehicle navigates on a continuous wire, which is embedded on the floor
- Antennas are located on the vehicle to detect the signal from the wire
- The encoders on the wheels of the vehicle calculate the distance for the movement
- Ideally, these types of navigation systems are used in retrofitments, repalcements, and expansions
Inertial Navigation Systems
- The co-ordinates, such as X and Y (usually, magnets), are embedded on the floor as per the requirement
- The points are detected by the sensor on the vehicle, as it passes over the reference point, and the gyroscope present in the vehicle measures and maintains the vehicle's movement
- The wheel encoder calculates the distance traveled by the vehicle
Order Picking Technologies
RF Picking
- Also referred to as mobile scanners, and are used to wirelessly read bar codes of products, which are to be picked in a warehouse
- ERP system sends alert to the scanner, if the wrong product is scanned or picked
Pick-to-Light
- LCD display device at each pick slot, connected by a data cable to a central ERP, indicates item to be picked
- Each LCD display unit will have buttons, like confirm, error, and pick, ready against an LED
Voice-Directed Picking
- Picking involves an ERP system, a dedicated VDP server, and a headphone and microphone with the picker
- The picker sends voice command to confirm location and product, error message is sent by ERP via VDP, if the error in product picked
Carousels/ASRS Picking
- A combination of both automated and semi-automated picking (carousels), is used, depending on the SKU's pick frequency
KPI for Material Handling and Storage
Material Handiling
General Practice
- Warehouse operations are capable of handling the current needs, but not designed properly for the seasonal growth
Good Practice
- The material handling operations are on well-ordered staging areas, clear aisles, and with clear market location, and capable of handling future tasks
Best Practice
- Effective and flexible material handling capability, with automation process, tailor made for current and future business needs
Put Away
Common Practice
- Put away locations are selected by WMS, with paper-based transaction process, and product may be staged for put away
Good Practice
- WMS selects the put away location, with a defined staging area, supported by put away zone. RF-based transactions are limited
Best Practice
- Put away locations are selected by the system, based on minimum time and product velocity
- The RF transactions are on a real-time basis, and the clearly defined staging areas are supported by put away zone and travel time
Interesting Reads:
Discover the world of market intelligence and how it can elevate your business strategies.
Learn more about how market intelligence can enable informed decision-making, help identify growth opportunities, manage risks, and shape your business's strategic direction.
Get Ahead with AI-Enabled Market Insights Schedule a Demo Now
