CATEGORY
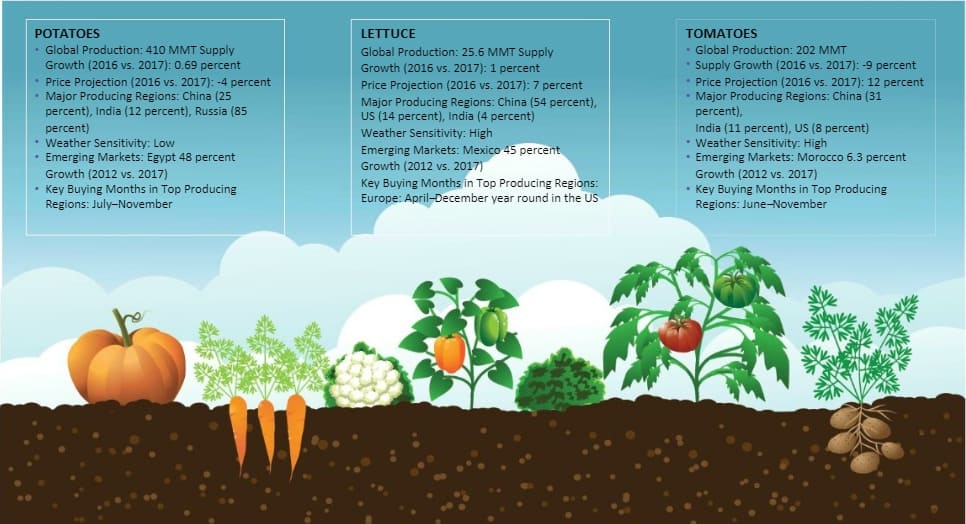
Vegetables
vegetables are exhibiting an upward trend, owing to shift in consumer's preference for foods that promote health and wellness. The top consumed vegetables globally in QSR and processing sector are Potatoes, Lettuce, Tomatoes, Onions, Beans and Chillies/Peppers.
Beroe LiVE.Ai™
AI-powered self-service platform for all your sourcing decision needs across 1,200+ categories like Vegetables.
Market Data, Sourcing & Supplier Intelligence, and Price & Cost Benchmarking.
Schedule a DemoThe World’s first Digital Market Analyst
Abi, the AI-powered digital assistant brings together data, insights, and intelligence for faster answers to sourcing questions
Abi is now supercharged with GPT4 AI engine. Enjoy the ease of ChatGPT, now on Abi
Vegetables Suppliers
Find the right-fit vegetables supplier for your specific business needs and filter by location, industry, category, revenue, certifications, and more on Beroe LiVE.Ai™.
Schedule a Demo


Use the Vegetables market, supplier and price information for category strategy creation and Quaterly Business Reviews (QRBs)
Schedule a DemoVegetables market report transcript
Vegetables-Procurement Insights based on Seasonality
Prices can be expected to be the lowest during harvest and post-harvest periods and higher during off-season. Ideally buyers could capitalize the low price periods and procure a higher share of their raw materials requirement and secure contracts that ensure a steady supply throughout the year. Bulk buying would incur additional costs like cold storage and inventory maintenance and spoilage losses. The buyer should also anticipate the surge in demand during the harvest periods, which could push prices up slightly and plan their procurement strategy accordingly.
Potatoes - Global Supply Analysis
-
The potato market in Europe is now clearly divided between north and south. In the countries where the impact COVID-19 is high, the demand is rising, but especially for local products. The demand in Italy has tripled for a short time at the start of the pandemic, and Spanish growers are barely able to keep up with the demand
-
In North America, there is uncertainty about the availability of potatoes for the market, while in Oceania the weather conditions have resulted in a lower yield per hectare
-
Potato growers in the US, reduced acreage by around 8 percent since 2014, in an attempt to improve market prices, which dipped steeply owing to surplus production of potatoes, proving unprofitable for growers
-
Processing potatoes, which account for about 12 – 15 percent of production is expected to display the fastest demand growth, particularly the frozen fries sector. Fresh potato consumption is estimated to gradually decline in the long term
-
A rise in demand for starch potatoes can be expected to increase post the removal of the EU sugar quota in 2017, with an expected increase in production of starch-based sweeteners
Potatoes - Global Trade Dynamics
-
The NAFTA renegotiation and US-China trade conflict will continue to impact potato trade in the coming years, with the U.S. and China competing for alternate markets for exports
- Mexico's tariff of 75 percent on the US potatoes post the NAFTA renegotiation is likely to lower potato exports from the US significantly in the coming year
- China does not allow imports of fresh potatoes, owing to SPS (Sanitary and Phytosanitary) concerns
- The removal of MEP (Minimum Export Price) of $360/ton in December 2016 boosted exports. India contributes to only about 1 percent of global exports despite being the second-largest producer
- Netherlands and Belgium are the leading importers of potatoes globally. More than 65 percent of the imports are consumed by the processing sector
- Malaysia, Russia, Vietnam, and Pakistan account for about 62 –65 percent of China's exports. The major export destinations of the US potatoes are Canada, Mexico, Japan, and Taiwan
Lettuce - Global Supply Analysis
-
Lettuce production in major producing regions, like Europe, is expected to witness a favorable season, supported by a cold spring. With the end of the season for Spanish lettuce, the Dutch lettuce is likely to have a fairly good demand
-
The recent outbreak of E. Coli in romaine lettuce has caused withdrawal from markets, which has narrowed the supply of lettuce and increased demand for other lettuce varieties significantly
- Despite low supplies, a dip in demand, due to an E. Coli breakout in Romaine lettuce is likely to maintain a weak market, lowering grower returns considerably
- The beginning of 2017, had a higher demand than supply, owing to the impact of heavy rains in major growing regions like the EU and drought in parts of the US
- March – April 2017 witnessed a surplus production, leading to a price crash and top exporters like Spain destroyed more than 50 percent of the produce, owing to unprofitable market
- As of September 2017, supply and demand has been stable and is expected to remain so in the upcoming year, if good growing conditions prevail
- Given the vulnerability of lettuce growing, an increasing number of indoor lettuce farming practices are being adopted by progressive farmers, which could boost production significantly in the upcoming years, ensuring a well-supplied market
Lettuce - Global Trade Dynamics
-
Japanese Ministry of Health has asked to hold back U.S. imports of romaine lettuce until FDA or CDC notifies the changes in regulatory status for romaine lettuce. The U.S. accounts for more than 90 percent of Japanese lettuce imports with a value of about $2.5 million in 2017
-
The ongoing US-China trade conflict has created opportunities for neighboring markets like Australia which could witness access to China markets for their lettuce
-
Spain and the U.S. are the leading suppliers of lettuce, accounting for about 36 percent and 15 percent of the world’s lettuce exports, respectively. The fastest emerging players in the export market are Mexico and Lithuania
-
Canada, Mexico, Japan, Korea, and Saudi Arabia constitute about 90 percent of the US’s lettuce exports, whereas Spain’s lettuce exports cater to the EU market primarily
-
The trade embargo by Russia, which accounts for about 40 percent of Turkey’s lettuce exports, have impacted Turkey’s trade volumes, which is scouting for alternate markets for its lettuce
-
Also, detection of “flower thrips” in Turkey’s lettuce, brought down the country’s exports further in 2015/2016
Tomatoes - Global Supply Analysis
-
The tomato market is quite unstable due to unprotected cultivation shifting from Northwestern Europe to Southern Europe. The acreage devoted to the crop in Southern Europe has been declining for years and this year there has been a reduction of between 10-20 percent
-
The U.S. Department of Commerce announced a withdrawal from the Tomato Suspension Agreement, which could have major financial consequences for Mexican tomato growers with higher costs, including a 17.65 percent tariff for Mexican tomatoes
-
In the U.S., the oversupply and weak demand for processing tomatoes after 2 years of increased production has led processors to decrease contract tonnage by nearly 8–10 percent, making it unprofitable for growers
-
China, the U.S., and Italy are the leading producers of processing tomatoes. About 60 percent of Italy’s crop was damaged due to bad weather, which would lower supplies and could improve the market situation in terms of returns
-
With the planned reduction in acreage and depleting inventories of processors by the end of 2017, the market can be expected to improve for both growers and processors
Onions - Global Supply Analysis
-
Overall, the supply of onions in 2020 is expected to remain firm, supported by shrinking output, reduction in acreage in the major growing regions and export markets, like the U.S., Canada, and Europe
-
Despite a supply glut in markets, like India, unfavorable weather in markets, like Europe and the U.S., are likely to lower onion supplies in the ensuing season
-
India seems to be getting quieter now that two Indian regions will soon deliver a new harvest. This is reducing the import of onions. Onion cultivation is expected to increase by 7 percent this year
-
Increased cultivation, owing to previous year’s high prices and damage due to hailstorm, led to a surplus of red onions, but of poor quality, which reduced farmer’s returns
-
The lowered production in some major growing regions could offset the oversupply situation and create a favorable market condition for onion suppliers
-
China’s production volume was lower by around 20 percent, owing to spring cold and hailstorm damage of onion crop
Interesting Reads:
Discover the world of market intelligence and how it can elevate your business strategies.
Learn more about how market intelligence can enable informed decision-making, help identify growth opportunities, manage risks, and shape your business's strategic direction.
Get Ahead with AI-Enabled Market Insights Schedule a Demo Now