CATEGORY
Sugar
Sugar is produced from Sugarcane / Sugar Beet andis widely used in Food & Beverage and personal care industry.
Beroe LiVE.Ai™
AI-powered self-service platform for all your sourcing decision needs across 1,200+ categories like Sugar.
Market Data, Sourcing & Supplier Intelligence, and Price & Cost Benchmarking.
Schedule a DemoCategory Alerts
Sugar prices soar to 11-year highs due to decreasing global supplies
April 17, 2023US sugar purchasers from the downstream sectors are seen rushing to contract sugar to cover their procurement for 2023/24
April 04, 2023EU sugar beet acreage is expected to contract 3% after EU court ruling on pesticide ban
April 04, 2023Become a Beroe LiVE.Ai™ Subscriber to receive proactive alerts on Sugar
Schedule a DemoSugar Market Monitoring Dashboard
Understand the correlation between costs, margins, and prices impacting your category on a real time basis on Beroe LiVE.Ai™
Schedule a DemoSugar Industry Benchmarks
Savings Achieved
(in %)
The average annual savings achieved in Sugar category is 5.00%
Payment Terms
(in days)
The industry average payment terms in Sugar category for the current quarter is 76.9 days
Compare your category performance against peers and industry benchmarks across 20+ parameters on Beroe LiVE.Ai™
Category Strategy and Flexibility
Engagement Model
Supply Assurance
Sourcing Process
Supplier Type
Pricing Model
Contract Length
SLAs/KPIs
Lead Time
Supplier Diversity
Targeted Savings
Risk Mitigation
Financial Risk
Sanctions
AMEs
Geopolitical Risk
Cost Optimization
Price per Unit Competitiveness
Specification Leanness
Minimum Order Quality
Payment Terms
Inventory Control
The World’s first Digital Market Analyst
Abi, the AI-powered digital assistant brings together data, insights, and intelligence for faster answers to sourcing questions
Abi is now supercharged with GPT4 AI engine. Enjoy the ease of ChatGPT, now on Abi

Use the Sugar market, supplier and price information for category strategy creation and Quaterly Business Reviews (QRBs)
Schedule a DemoSugar market frequently asked questions
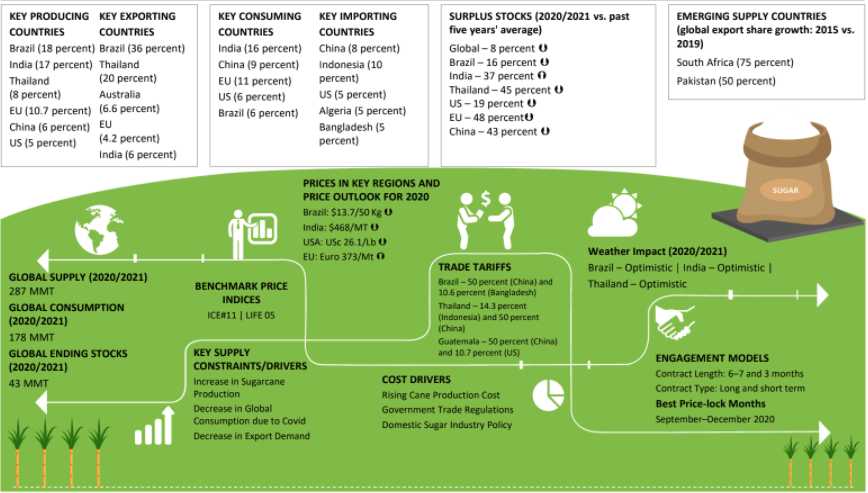
While the global sugar supply reached 287 million metric tons (MMT) during 2020-21, the global consumption pegged 178 MMT within the same timeline.
As per the research, global sugar production is expected to grow at around 13% year on year (Y-o-Y) over the forecast period.
China has been the major sugar importer; however, the imports have dropped due to policymakers' restrictions. At present, Indonesia is at the driver’s seat in global sugar imports.
Increasing sugarcane prices, a conducive regulatory environment, and favorable domestic sugar policies are primarily driving the global sugar market revenue.
The European Union (EU), Thailand, China, and India witnessed a significant surplus supply of sugar during 2020-21 compared to the previous five years’ average.
Sugar manufacturers are turning to South Africa and Pakistan for potential growth avenues. Export share in both the countries surged to 75% and 50% respectively in 2019 compared to 2015.
Sugar prices are majorly affected by the raw material costs, which make up for around 4/5 of the overall production expenses.
Sugar imports in the EU have declined, owing to the encouraging sugar production quotas in the region. In addition, sugar stocks in the EU are likely to increase to 2.2 MMT compared to the previous year with solid cane and beet yield.
Sugar market report transcript
Global Market Outlook on Sugar
-
The current global sugar market is witnessing a surplus in supply over demand, as higher output is expected from top producer Brazil in the current season. Estimates for 2022/23 denote a surplus of 5.57 MMT, driven by an expected recovery in Brazilian output, coupled with higher volume from Asia. While regional tightness is anticipated in the US and Europe, on the account of adverse weather, high energy costs and shifting acreage to grains & oilseeds tightening supply.
Global Supply–Demand Analysis
-
The current global sugar market is witnessing a period of seasonally high supply, amid the harvest season in key producing regions. While initial estimates for 2022/23 denote a surplus of 5.57 MMT, driven by an expected recovery in Brazilian output, coupled with higher volumes from Asia. While regional tightness is anticipated in the US and Europe, on the account of adverse weather, high energy costs and shifting acreage to grains & oilseeds tightening supply.
Sugar Production by Country (2022)
-
The International Sugar Organization (ISO) in its latest quarterly bulletin projecting a global surplus of 5.6 MMT in 2022/23, compared with a deficit of 1.3 MMT the previous season. While sugar output in Brazil’s center-south (CS) region is likely to increase this season as against earlier expectations due to more favorable weather conditions and domestic fuel tax exemptions – with the Brazilian agency Conab recently raising its Brazil 2022/23 sugar production estimate to 36.4 MMT from the prior estimate of 33.9 MMT
-
The good progress of sugarcane harvest in India and Thailand is seen to raise global sugar availability with the industry group Czarnikow upward revising estimates of global sugar production for 2022/23 by 0.8 MMT to 179.2 MMT with further upside potential
-
Regional tightness is anticipated in the US and Europe, on the account of adverse heat wave conditions and shifting acreage to grains & oilseeds exacerbated by the Russia-Ukraine war and high input cost tightening supply
Global Sugarcane and Sugar Beet Production
-
The global sugar market constitutes majorly of cane sugar whose output represents approx. 77 percent of the total sugar output, while the remaining 23 percent is sugar derived from beet; while cane sugar output is estimated to rise 1.8 percent in 2022/23, beet sugar output is projected to remain tight amid lower volumes expected from Europe and the US
-
The global cane sugar market is dominated by Brazil, India and Thailand and accounts for approx. 77 percent of the total global sugar output
-
Global cane sugar production is projected to rise marginally by 1.8 percent Y-o-Y in 2022/23 to 144.6 MMT – with higher output in India and Thailand adding to the recovery in sugar volumes expected from Brazil, with higher diversion of sugarcane to sugar anticipated instead of ethanol
-
The global beet sugar market constitutes approx. 23 percent of the total global sugar output with Europe, US, Russia, and Ukraine leading in the market share
-
Global beet sugar production is estimated to remain stable at 38.5 MMT with downside risk expected, mainly due to adverse heatwaves in key producing regions of Western Europe and the US, coupled with shifting acreage to other crops such as grains & oilseeds whose prices have surged exacerbated by the Russia-Ukraine war. While high input costs such as for energy and fertilizers is seen to result to restrict output
Trade Dynamics : Sugar
-
Global raw and refined sugar exports are witnessing a recovery over the lower volumes experienced, due to suppressed global demand during the pandemic, with Brazil leading the market share for global sugar exports while India is seen to curb exports
-
A recovery in Brazilian sugar output for 2022/23 is estimated to raise export volumes by 8.7 percent
-
While record high Indian sugar exports which reached 11 MMT during the current season is seen to reduce during 2023 and be split between two tranches depending on the domestic market situation with the first tranche set at 6 MMT till May 2023
-
Mainly, the Chinese refiners import raw sugar for refining and selling them to food & beverage industry
Sugar Cost Structure Analysis
-
On an average, 70–80 percent of the total cost is incurred by sugarcane/sugar beet procurement in all the major sugar producing countries, except Brazil, where sugarcane contributes to only 55 percent of the total cost. Brazil is the most cost-effective country in producing sugar. While the prevailing surge in agricultural input cost inflation such as for fertilizers and energy is seen to keep production costs elevated over 2022/23 across regions especially in Europe due to the high dependency on natural gas as an energy source for refining
-
Sugarcane is the only feedstock, which has a high impact on sugar production. Price of sugarcane is fixed by the government, depending upon sugar prices and average sugar recovery rate
-
Minimum support price of sugar cane/sugar beet must be tracked to understand the price movements of sugar and better negotiate with suppliers
Porter’s Five Forces Model: Sugar
Supplier Power
-
Sugarcane and sugar beet prices are regulated in most of the key sugar producing regions within minimum chances for negotiation
-
Most of the leading sugar mills ensure raw material supply through contract farming
-
However, prices fixed are based on sugar recovery rates. Premiums are paid, in case of higher than average recovery rates
Barriers to New Entrants
-
Cost of establishing a sugar refinery is high, and it requires the government approval
-
Raw material procurement is completely regulated, and it is a big challenge for new entrants in most of the key producing countries
-
Sugar prices are highly volatile, and returns are not guaranteed
Intensity of Rivalry
-
The supplier market is stable, as it is dominated by sugar cooperatives, who own refineries and have predefined sugarcane acreage allocated to them
-
Entry of a new player in the supplier market is controlled by the government regulations. There is no trend toward consolidation
-
Difficult to add capacity in the short run, as high investment is needed to open a new plant
Threat of Substitutes
-
HFCS and artificial sweeteners are rapidly gaining popularity. Also, as corn is cheaper than sugarcane in production, HFCS is more cheaper than sugar in major corn producing countries, like the US
-
Growing consumer's health awareness is shifting focus toward sugar-free sweeteners, such as stevia and other artificial sweeteners
Buyer Power
-
Although food & beverage industry is the largest buying segment of sugar, buyer power within this segment depends purely based on volume
-
There is a less scope for negotiation on prices, as country-level or global-level price benchmarks are used to fix prices
-
Length of contract is directly proportional to volume procured
-
Cost of shifting to another supplier is negligible
Innovations/Trends : Sugar
Innovations in the sugar industry globally are inclined toward the genetically modified sugarcane crop and sustainable farming. New techniques, in order to increase the yield and productivity, are also being researched in the leading sugar producing countries.
Australian Sugar Industry
-
In Herbert valley cane growing region, tropical North Queensland, GIS is used across the entire supply chain (from farm to factory) of sugarcane to track the yield and loss to increase the productivity and the profitability
Indian Sugar Cultivation
-
In Madhya Pradesh, innovations through spacing techniques have increased sugar recovery rates
-
135 cm of spacing was followed in planting sugarcane in this region against the recommended spacing of 60–90 cm
-
This increased spacing led weed controlling easier, resulting in improved productivity and sugar recovery
GM Sugarcane Crop
-
Drought-resistant genetically modified sugarcane crop is under research in India
-
Indian Council Agriculture Research and Sharad Pawar-led Vasantdada Sugar Institute are involved in this project
-
The successful crop will require less amount of water for its growth, which is expected to reduce the crop deficit situation in the future
Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative
-
It is another innovation in the Indian sugar industry to reduce the ecological footprints in sugarcane cultivation
-
It is getting popular among the farmers, and these techniques are being practiced
Interesting Reads:
Discover the world of market intelligence and how it can elevate your business strategies.
Learn more about how market intelligence can enable informed decision-making, help identify growth opportunities, manage risks, and shape your business's strategic direction.