
Are Promotional Speaker Programs Going the Distance?


Abstract
Among the various marketing and communication strategies used by pharmaceutical companies, one of the most popular is speaker programs. These events are largely used for promotion and informing healthcare professionals about the therapeutic areas, diseases, and drugs the companies are working on. Interactions during these events help professionals stay up-to-date on the latest developments in the industry. In the past few years, speaker programs have become a topic of controversy for various reasons, such as companies misusing the programs, increased regulations imposed by various U.S. government authorities, changes in the way the programs are conducted, and shifts in trends. This white paper provides an overview of the types of speaker programs used, the risks and regulations around conducting these programs, and their impact on the industry. It also touches upon the alternatives used by companies and the steps they have taken to ensure complete compliance on aspects that affect their business.
Introduction
Speaker programs are held by pharmaceutical companies where pre-approved materials are used to educate healthcare professionals. They are important for the industry, as the forums bring value in terms of exchanging the right information among medical professionals. They also help physicians stay up-to-date on information about new medicines, new uses of medicines, the latest clinical data, appropriate dosing, and emerging safety issues. Companies have begun to use various speaker programs apart from the traditional face-to-face type. However, any program is expected to adhere to certain rules and. Non-compliance with these regulations has led companies to receive heavy penalties. Some common regulations to watch out for are the Sunshine Act, codes of ethics, financial compliance, and codes of interactions with healthcare professionals. Compliance with the prescribed regulations helps companies sail smoothly through the process.
Types of Speaker Programs Being Used in the Industry
- Face-to-Face:
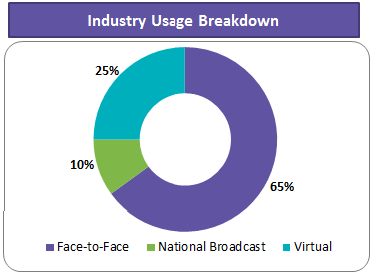
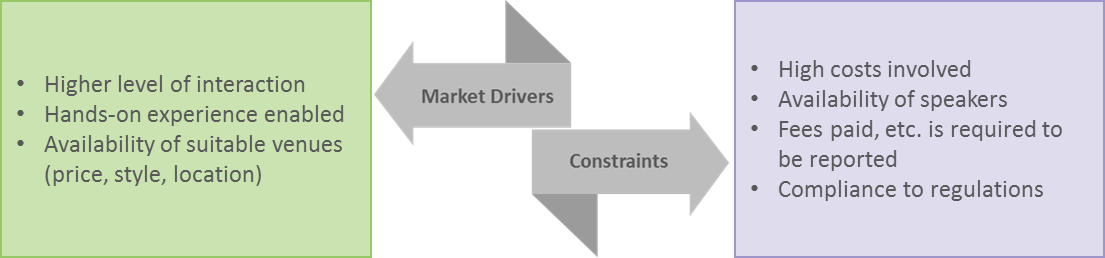
A face-to-face speaker program is a venue-based event where the attendees can interact with the group in-person. This is considered the most effective type of event for disseminating information. However, the downside is that participant attendance is often very low, and the costs are higher than other types. Having said that, they are the most widely adopted form of speaker programs in the industry.
- Virtual Speaker Programs:
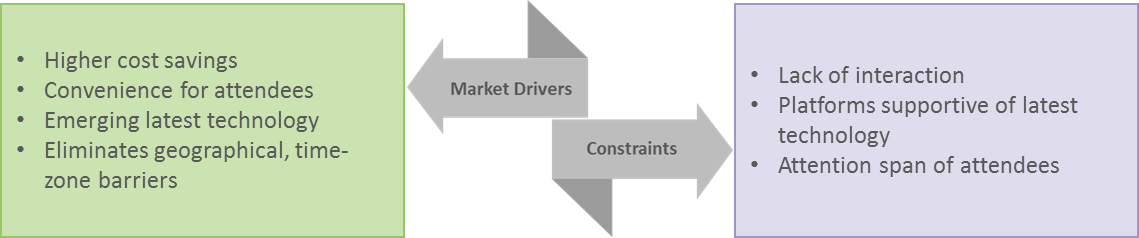
Virtual programs are a medium to achieve lower costs along with a larger audience reach, irrespective of geographical barriers. As an added benefit, the virtual approach allows speaker programs to be conducted in a more compliant format.
Companies and speaker bureaus have undertaken some simple steps to make virtual programs more successful and effective.
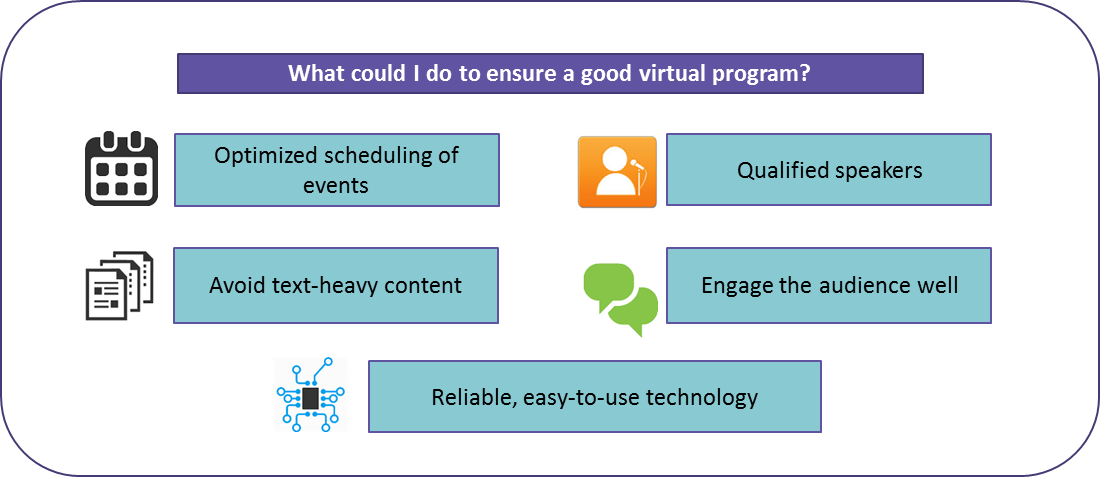
The acceptance of virtual programs in the past few years has been very good. They have provided exceptional value to brands in target audience participation and cost per head. Many aspects contribute to the success of virtual meetings. They are: having a systematic planning process for the event, implementing easy-to-use programs, delivering engaging experiences, and the availability to choose between multiple time slots. Virtual speaker programs can be a primary channel for effectively connecting key opinion leader speakers with local clinicians while reducing marketing costs, improving compliance, and driving greater access for sales representatives.
- National Broadcasts:
Only 10 percent of the market uses national broadcasts. These types of events are not very popular, as they are expensive, require speakers of a global standard and high-quality original content. This type of speaker program is mostly used during certain big occasions involving new product launches, etc.
Repercussions of Non-Compliance
In recent years, pharmaceutical companies have been stumbling over various risks and regulations while conducting speaker programs. The past 5–10 years have seen the world’s leading pharmaceutical companies pay billions of dollars of penalties for rules violations. Some common regulations are:
1.Anti-Kickback Violations:
This statute aims to curb fraud in the healthcare system by professionals who provide services and expect benefits in return. The Anti-Kickback Statute states that anyone in the healthcare industry who consciously and deliberately accepts a fee or remuneration of any kind, or offers the same, with the intention of manipulating the course of medical decision-making, is liable to punishment.
What Attracts Penalties?
Acts of various kinds attract penalties under the Anti-Kickback Statute. Some of these include:
- Carrying out advertising or marketing activities for promoting healthcare provider brands
- Participating in affiliate programs or pay-per-click commissions
- Working out promotion agreements with multiple companies
- Taking part in sponsorships
- Working out strategic alliances with healthcare providers
- Licensing content or technology
- Selling a healthcare provider's brands of products or services
- Taking a cut of the advertising revenue
2. Sunshine Act:
‘The Sunshine Act, also known as Open Payments, requires pharmaceutical, biologic, and medical device manufacturers (collectively, Manufacturers) to annually disclose to the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) all payments and other transfers of value (collectively Payments) furnished to U.S.-licensed physicians and teaching hospitals (collectively, Covered Recipients).’
What Must Be Reported Under the Sunshine Act?
- In-service meals; that is, meals accompanied by an educational presentation by a sales representative in a physician’s office
- Meals consumed at Promotional Speaker Programs, Investigator Meetings, Advisory Boards, and Product Theaters, provided the identity of the participants is known
- Any travel costs related to, but not limited to, speaker programs and advisory boards
- Fee-for-service arrangements such as consultant, speaker, or advisory board member
- Fee-for-service arrangements such as clinical trial investigator
- Grants
- Educational materials that are not intended for use by a patient
Along with the above regulations, companies should watch out for off-label promotions, codes on interactions with healthcare professionals, financial compliance, and codes of ethics. However, monitoring certain aspects could mitigate risks for the company at a higher level. The illustration below sets an outline.
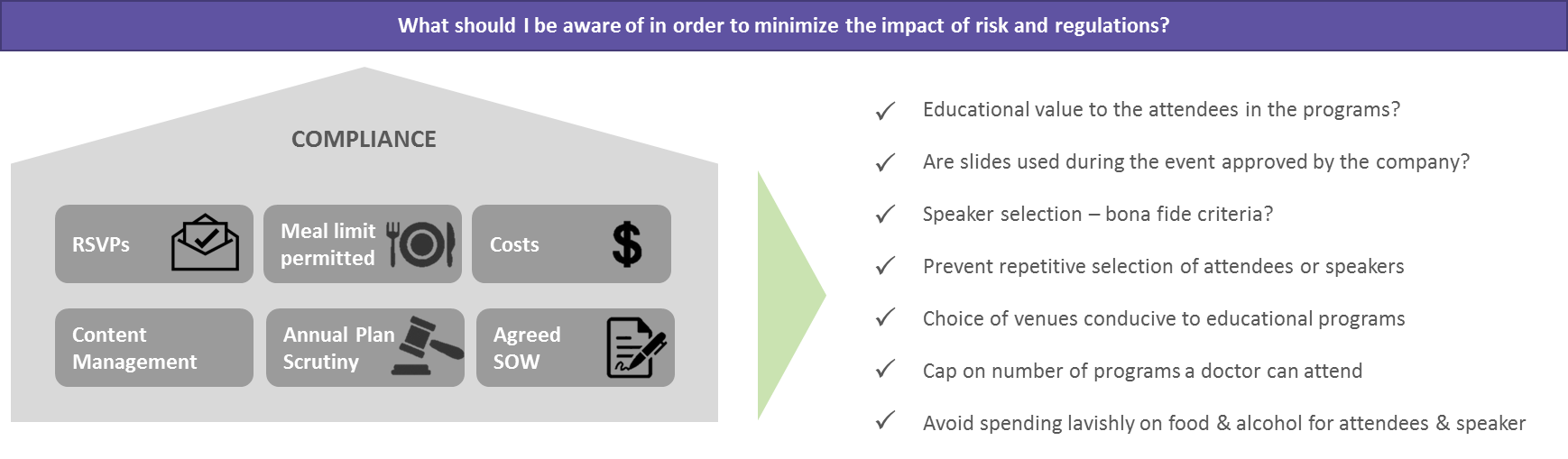
How Have Regulations Changed the Way Companies Look at Speaker Programs?
1.Adopting Rigorous Controls in the Existing Strategy:
Companies are establishing the following controls at various levels to avoid any breach of legal norms while conducting speaker programs:
- Ensuring there is a legitimate business need for educating healthcare professionals
- Reviewing internal policies
- Conducting periodic risk assessments to identify any hurdles that may come up
- Closely monitoring compliance with policies, and undertaking corrective actions in case of non-compliance
2. Considering Alternatives to Speaker Programs:
- Various forms of physician education:
- The industry is looking at various forms of physician education to disseminate product information.
- The industry is looking at various forms of physician education to disseminate product information.
- Therapeutic Committee Meetings:
- Other manufacturers are focusing on preparing their medical teams to present at payer pharmacy and therapeutics committee meetings
- Other manufacturers are focusing on preparing their medical teams to present at payer pharmacy and therapeutics committee meetings
- Direct-to-Consumer Marketing
3. Doing Away With Organizing Speaker Programs
Companies like GSK have withdrawn from most speaker programs to lower the risk of receiving legal warnings or lawsuits.
Some medical centers and health systems, like the Mayo Clinic, Stanford University, and the University of Wisconsin, are prohibiting their staff doctors and faculty from participating in promotional speaker programs.

Conclusion
Speaker programs form a vital part of any brand’s medical communication strategy. They are one of the most widely used, necessary components for the kind of two-way engagements they enable between healthcare professionals. Speaker programs have large impacts on prescribing patterns and awareness of the latest updates in the industry. However, they were subject to many disputes for various reasons, and several companies faced the brunt of penalties because of non-compliance with the set guidelines. During this period, many speculated whether speaker programs would end or go into the dark. Proving all those notions wrong, companies never turned their backs on these events because of the programs’ importance to the healthcare business. They found ways to reduce risks and build the programs in a compliant manner. They found ways of conducting the meetings in a more cost-effective manner, with less expensive speakers, smaller venues, and less travel. There was also a shift to web-based programs and Continuing Medical Education programs to supplement speaker programs. In conclusion, today’s trend is more focused on controls and thresholds for speaker programs, yet these have neither decreased the participation of healthcare professionals in industry-sponsored programs, nor the support for promotional programs by customers.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe






