Authentication tokens facilitate secure transactions in the banking Sector

Abstract
Introduction
For today’s banking industry, the Internet platform continues to be the most preferred channel for both corporate and retail banking given the prodigious growth of e-banking and the unimaginable penetration of smartphones. This development is driven by the banks’ desire to reduce costs as well as customers’ requirement to access bank services online anytime without any geographic constraints. The importance of Internet banking is obvious for several reasons. Firstly, online banking offers a cost efficient alternative to telephone and branch banking due to the relatively low capital and maintenance costs, and its fully-automated processing of all types of transactions i.e. simple to complex. Secondly, it offers unparalleled customer convenience by enabling 24-hour access to a wide range of services. Despite this win- win proposition, Internet banking is not without its own range of drawbacks. Foremost among these in recent years has been the cyberattacks on banking systems.
This paper discusses the reasons for adoption of an authentication solution and the problems associated with implementing such solutions across a global banking player.
Problem Statement
Consulting and managing bank accounts from home or any other place i.e. during travel, shopping, etc. has already proven to be very convenient for users. This is also convenient for banks which can then afford to have their employees in local offices focusing on value added services rather than basic retail banking operations. However, such online services raise the issue of security levels. For instance, confidentiality and privacy have been key issues while conducting banking transactions. In case of inter-bank transactions, the risk of theft has become imminent.
Global banks recognize the importance of strong authentication for their online customers. Online banking is losing around 20 million customers a year due to the fear of phishing attacks, fraudulent transactions and ID theft. Fraud is clearly putting online banking at the risk of collapse.
Solution
In the context of increasing cyber threat, normal static passwords are no longer secure enough and more secure methods are necessary to meet all the four security requirements: user authentication, data integrity, transaction confidentiality and non-repudiation. Authentication tokens are used to mitigate the above requirements.
Introduction
A lot of research is focused on the cyber-security of financial transactions, both from a cryptographic as well as from a computer security viewpoint. As a result, wholesale transactions are now relatively safe and secure.
However, the challenge today is to secure PC-based/Internet-based transactions as banking crimes such as phishing, online fraud, hacking, and malware implant has been far more frequent. These attacks are more prevalent in Internet banking systems of technology savvy countries such as the U.S. and UK.
Authentication tokens are one of the methods adopted by the banking industry to minimize security lapse. And success in implementing a secure framework using authentication tokens will require extensive collaboration among participants to ensure that banking consumers have a cohesive solution. Also, it should be a solution based on agreed upon standards, rules, and practices that ensure seamless interoperability regardless of the mobile device, mobile operating system (OS), financial institution (FI), payment network, merchant, or wallet provider involved in the consumer’s desired transaction.
Authentication tokens: an overview
For any online banking, the primary access control mechanism through Internet has been predominantly username and password. This basic, single factor authentication has become inadequate in the face of increased cyber fraud activities in recent years.
The alternate mechanism, which is comparatively more secure and widely adopted, is two-factor authentication. Two factor authentications are based on something that a user has (a physical device) and something that a user knows (a PIN number or password). A common application of two-factor authentication in everyday life is withdrawing money from an ATM. The user is required to insert their card in the ATM (something they have) and then type their PIN (something they know). By using some method/tool a user knows with something a user has (card/sms), the same level of authentication can be brought to the online world.
Authentication systems used in Internet Banking
The following are the four common classes of authentication schemes that are usually employed by banking institutions.
One-Time-Password (OTP) schemes: OTP is generated as passwords using pseudo- random generators or mathematical algorithms in order to authenticate online users. However, they offer no security against man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks.
Full Transaction Authentication: The OTP generated through mobile/mail to authenticate the transaction is cryptographically bound to the transaction data.
Partial Transaction Authentication: This is a “relaxed” form of full transaction authentication, where only part of the transaction data is required during authentication.
Types of tokens prevalent in the Banking Industry
- Authentication Tokens vs. Access Tokens
- Computed Token
- Decision Tokens and Obligatory Tokens
- Data Tokenization
- Hard Tokens and Soft Tokens
- Integrity Tokens vs. Trust Tokens
- Network Tokens
- Public Tokens/Private Tokens
- Risk Tokens
- Standardized and non-standardized tokens
- Subject Tokens vs. Resource Tokens
- Transaction Tokens
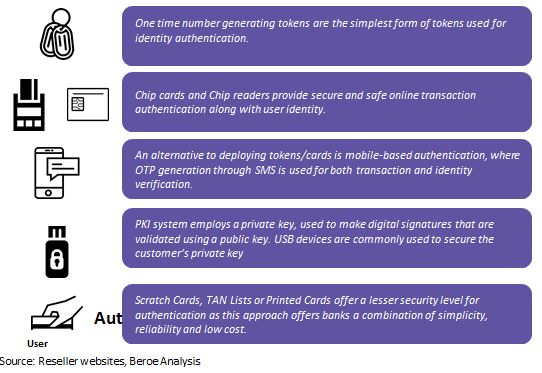
Most prevalent forms of authentication tokens
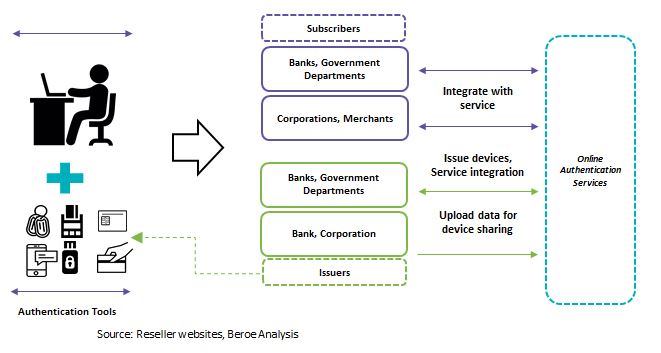
Next level of authentication-authenticator
Authenticator is a dedicated authentication server designed specifically for banking applications
- Independent modular architecture
- Best in class security module with firmware
- Stronger Administrative control for critical management tasks
- Tamper-evident logging
- Flexible token management
For an authenticator, it is crucial that the management of secret information is secure, be it a token key, or static password that is shared with the customer. Any compromise of these authentication secrets would be disastrous for the bank. An authenticator with strong technical and procedural controls can eliminate the threat of banking account compromises.
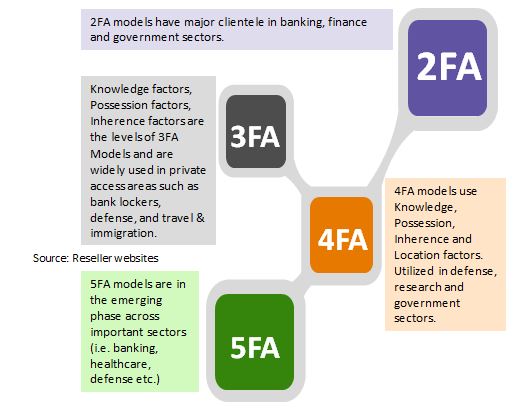
Multi-factor authentication tokens
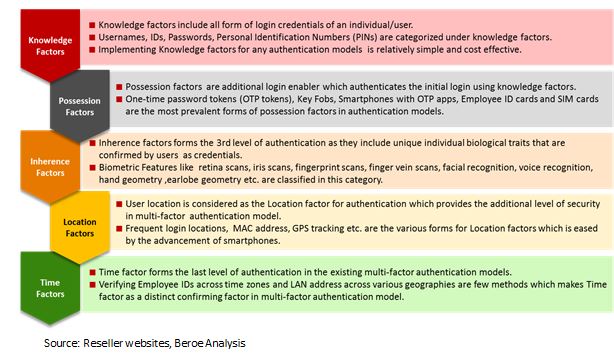
Various factors of authentication tokens
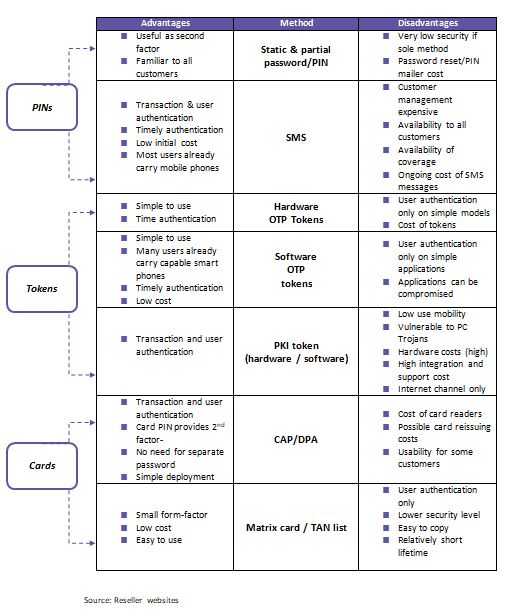
Benefits comparison of various authentication tokens???????
Conclusion
There is a growing need for more secure and better authentication methods as mere passwords are not enough for banking in this digital age. USB tokens, which are convenient, personalized and portable, offer better security as they combine encryption capabilities of a smart card with the versatility of the token.
However, two-factor authentication is still inadequate to deal with browser rootkit attacks. Despite stringent authentication methods, it is possible for cyber criminals to access information displayed on the banking portal such as account numbers, name, account balance and transaction details. A simple browser rootkit can leak all this information to an attacker who can use it to physically target rich users, steal identities, etc. To deal with this problem, banks need to carefully consider what they display on the browser besides offering various authentication measures to customers.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe