Shifting Geographies for the Cobalt Sulfate Market

Abstract
There is a global race to lock-up the supply chain for cobalt, which is expected to be in even greater demand as and when there is an increase in electric-car production.
Around 55 percent of the raw material cobalt is mined from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and is used to manufacture cobalt sulfate. The demand for cobalt sulfate is driven mainly by the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EV) and energy storage systems (ESS) with its major application in lithium-ion batteries
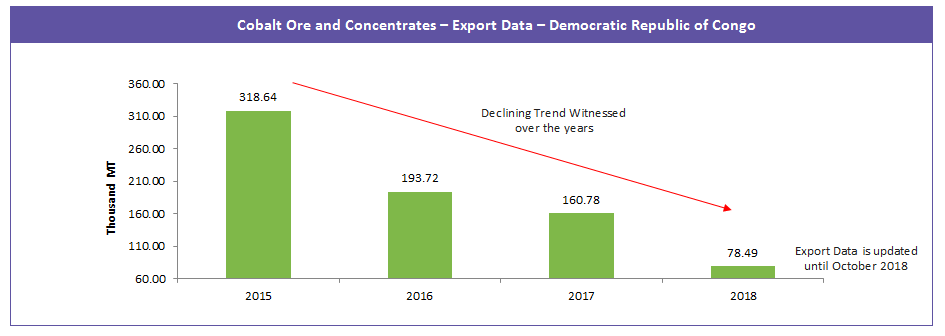
However, recent years have showcased a declining trend in the mining activities in the Congo region. This has created a looming tight supply situation, sky-rocketing the raw material cobalt price, which has directly affected the market scenario and pricing dynamics of upstream cobalt sulfate.
This article aims to provide purchasing managers with insights into the overall cobalt sulfate market dynamics, the reasons for the decline in cobalt mining in the Congo region, and possible alternate sources for procuring cobalt ore or cobalt sulfate
Global Cobalt Sulfate Market
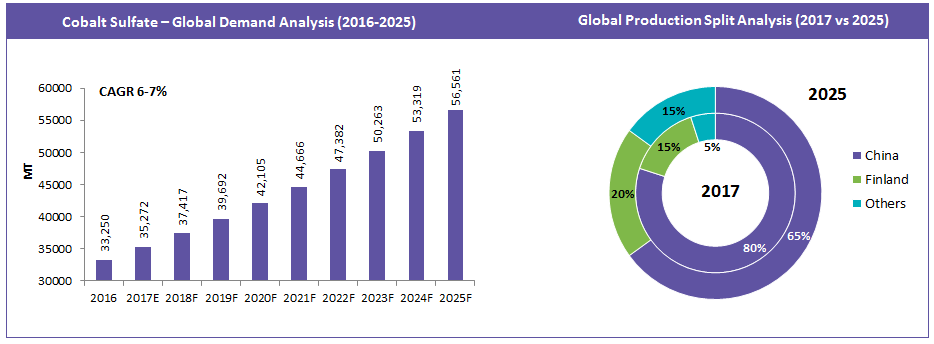
The cobalt sulfate market is driven mainly by the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EV) and energy storage systems (ESS) with its major application in lithium-ion batteries. The demand in 2017 was around 35.2 Thousand MT and is expected to grow at a rate of 6-7 percent until 2025.
Presently, ~75-80 percent of cobalt sulfate is refined in China and the majority of the remaining cobalt sulfate is processed in Finland. Moreover, the raw material required for this processing is obtained from a mine in the Congo, which is owned by a Chinese firm, China Molybdenum.
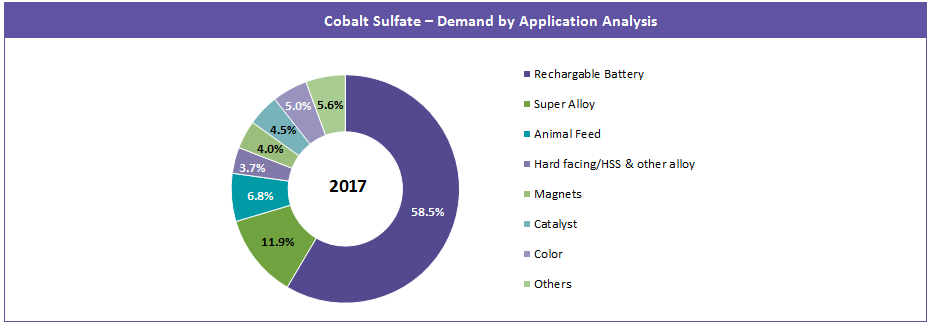
Talking about downstream applications, the rechargeable battery segment accounted for more than 50 percent of the share in the global cobalt sulfate market in 2017 because of its use in several growing applications like passenger EVs, consumer electronics, and ESS.
Apart from the battery segment, a major share of the cobalt sulfate industry is accounted for by the super alloys segment because of their applications in aircraft manufacturing.
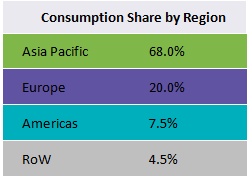
Asia is the leading consumer of cobalt sulfate, accounting for approximately more than half of the share of the global market until 2025. This is mainly because China is scrambling to roll out electric vehicles to reduce pollution thereby increasing domestic demand for cobalt sulfate.
Europe was estimated to be the second highest consumer of cobalt sulfate in 2017, majorly supported by Finland and Belgium supplying cobalt sulfate in the region.
Latin America, closely trailed by North America, is projected to provide growth opportunities in the forecast period owing to increasing consumption of cobalt sulfate as animal feed.
As mentioned earlier in the article, The DRC is the largest source of cobalt ore, which is used to produce cobalt sulfate. However, production is currently facing a few issues because of regulations and human-right violations and this is expected to affect the cobalt sulfate supply in the years to come. Below are a few regulations that are hampering the supply.
Congo – A Less Favorable Sourcing Destination
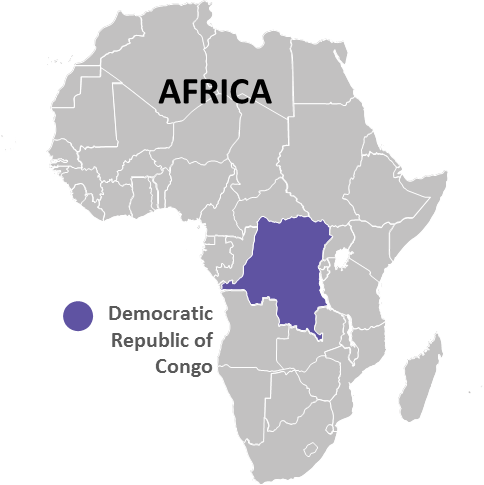
The DRC is the largest active region for cobalt mining in the African region. Presently, cobalt sulfate is sourced from the copper belt of the DRC and Zambia.
The growing EV market is projected to create a huge demand for cobalt sulfate; however, raw material cobalt availability from the Central African region is likely to witness supply chain issues vulnerable to geopolitical risks of various kinds, leading to limited availability of raw material cobalt.
These issues range from laws/policies setup by the DRC government itself to matters of employment of child labor in the mines.
Regulations and Governance Instability
-
The DRC government have regularly imposed and are continuing to impose restrictions on the export of ores & concentrates mainly to boost the downstream processing in the country.
- The government recently voted to raise taxes and royalties on profits and metals produced, including cobalt, causing the prices to soar by 110% on the back of surging demand from the EV market. Congress in the DRC recently passed a revised mining law that is expected to increase taxes on cobalt and other metals. This news has left miners concerned about its effect, which is projected to push cobalt prices.
- The country has been negotiating mining contracts with other countries, which has led to a rise in the mineral cobalt price and subsequently cobalt sulfate prices. The country’s state-owned mining company, Gécamines SA, has also been pushing the government to renationalize the entire mining industry. However, Glencore’s subsidiary in the DRC will temporarily halt cobalt exports from its Kamoto Project after finding high levels of uranium in the ore.
Labor Issues and Supply Chain Risks
-
Several human rights groups have claimed that some cobalt from the DRC could come from mines that adopt child labor along with horrendous conditions for adults, thereby raising additional concerns about sourcing within the industry.
-
This is likely to lead to added shortage in supply and/or further rise in cobalt sulfate prices.
The demand for cobalt sulfate is on the rise with the growing demand for electric cars. The shift to EV is happening much faster than anticipated and the reason is because of the rapid evolution of a global supply chain for key components in lithium-ion batteries. China is a key hub for EVs and electric storage unit manufacturing with plans to add more than 150 gigawatt hours of production in the next three to four years, thereby tripling current capacity.
The anticipated boom in the EV sector driven by China is likely to create huge demand for cobalt which is subsequently likely to put more pressure on the cobalt sulfate supply.
So with the DRC likely to be out of the sourcing picture, sourcing managers should ideally start looking for alternate cobalt sourcing destinations. Let us have a look at the possible sourcing options that are likely to be available by 2025.
Conclusion
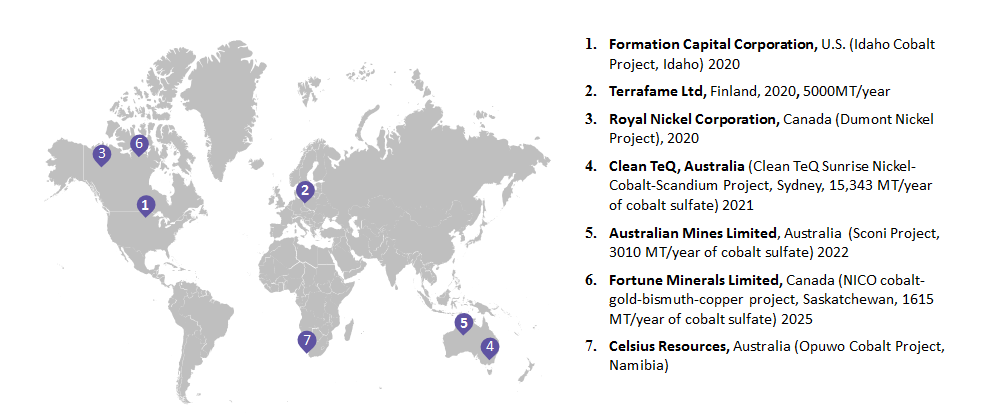
With the cobalt sulfate supply expected to witness a rough patch because of the reduction in exports of cobalt ore from the DRC, together with an anticipated increase in demand for cobalt sulfate from the EV sector, purchasing managers have to look for better sourcing options to safeguard their supply in the coming future.
Mentioned below are a few potential sourcing destination alternatives:
Alternate Sourcing Destinations
Mentioned below are the locations of new plants and the years that they are expected to come online. New refining plants are already under development and are undergoing pre-feasibility stages.
References
- Asian Metals
- Industrial Minerals
- Cobalt Weekly
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe







