
Lithium Ion Battery Price, Trend and Cost Structure (Li-ion)


Abstract
A Lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery in which lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when charging. Li-ion batteries use an intercalated lithium compound as one electrode material, compared to the metallic lithium used in a non-rechargeable lithium battery. Lithium is the lightest of all metals, has the greatest electrochemical potential and provides the largest specific energy per weight. Rechargeable batteries with lithium metal on the anode could provide extraordinarily high energy densities. The prices of Lithium-ion batteries have come down by ~80 – 85 percent in the last decade. It is also expected to breach $ 100/kWh barrier in 2020 and $ 60/kWh barrier in 2030 due to technology advancement and economies of scale. The average prices of batteries have been dropping much faster than the forecasted prices in past decade and it is expected to do the same in the next decade.
Price Trend & Cost Structure
-
A lithium-ion battery cell for a smartphone costs the device OEM somewhere between $2 to $4 depending on its capacity and other design attributes. It constitutes about 1 to 2% of the entire cost of the mobile device. In contrast, a lithium-ion battery for an electric vehicle can range between $7,000 and $20,000, making it by far the most expensive item in the cost of the vehicle.
-
The prices of Lithium ion batteries has come down ~80-85 percent in the last decade, the average price of battery is around $ 176/kWh. Various studies point out that the average battery prices could come down as much as $ 60/kWh due to economies scale and technology improvements
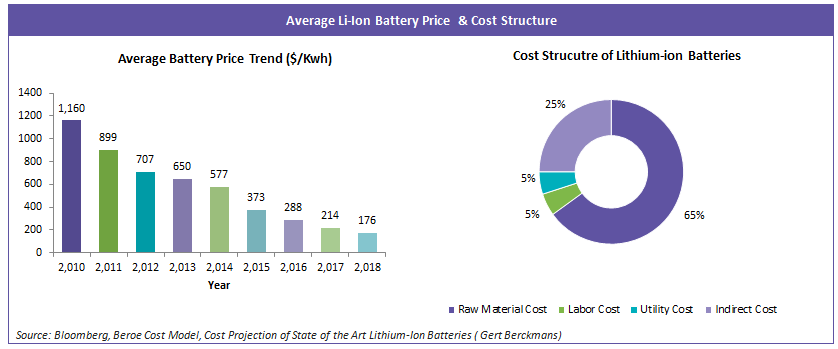
- The Raw material cost includes the cost of electrodes, electrolyte, separator, cell assembly, module assembly and other materials
- Cost Drivers: The prices of Lithium, Cobalt & Nickel have less than ~ 16 percent cost contribution towards the average battery prices. Hence, even if the prices of Lithium, Cobalt & Nickel doubles the impact on cost will be less than ~ 16 percent. The prices of separator, electrolytes and assembly modules contributes around ~50 percent of average prices
- Applications: The Lithium ion batteries are being used in various applications like battery electric vehicles, portable electronics & aerospace applications
- Production Process: Lithium ion batteries are manufactured on a large-scale production line consisting of electrode formation, stacking, inspection and packaging processes. The agitator mixes the battery materials coated onto the lithium ion battery’s electrodes. The coater applies aluminum foil oxide on the cathode, carbon coated copper foil on the anode. The cathode, anode, and separator, which have been coated and dried, are each slit to a constant width using a cutter knife. The cathode, anode and separator are stacked and wound into a cylindrical or rectangular shape to manufacture the battery cell.
- Investment Capital: Lithium ion Battery manufacturers like LG chem, Tesla, Lithium Werks B.V. & BYD are continuing to adding capacities in terms of setting up Giga factories around the world. For instance, BYD of China has invested $ 1.49 billion on a 20 GWh gigafactory in China
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) is the main growth driver for the Lithium ion battery cell packs, which is expected to replace ~ 50 percent of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles by 2040
- Due to lack transparency in manufacturer’s margin, the procurement organizations could be paying higher than actual prices of Lithium ion batteries
- More Pollution – The mining of feedstock for batteries creates more pollution to the environment. Some studies suggest Lithium-ion batteries emit ~ 74 percent more CO2 than an efficient conventional internal combustion engines vehicles
Conclusion
- The average prices of Lithium - ion batteries will continue to decrease faster than predicted prices. It is mainly due to the technological advancements and economies of scale. The Lithium – ion battery suppliers around the world are investing in ultra-large or gigafactory with huge capacities anticipating demand in battery electric vehicles like cars, buses and trucks.
- Due to transparency in supplier margin, procurement organizations could be paying higher than the actual prices. The prices of Lithium, Cobalt & Nickel has less contribution towards the final price than other materials like separator, electrolytes & module assemblies.
References
- Beroe Cost Model
- A Behind the Scenes Take on Lithium-ion Battery Prices – Bloomberg,
- Cost Projection of State of the Art Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles Up to 2030 - Gert Berckmans
- Lithium Batteries' Dirty Secret: Manufacturing Them Leaves Massive Carbon Footprint – Bloomberg
- Fact Sheet - Plug-in Electric Vehicles - Environmental and Energy Study Institute
- The financial dilemma of battery manufacturers - https://qnovo.com/financial-dilemma-of-battery-manufacturers/
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe







E