
Impact of Pestalotiopsis fungal disease on NR supply chain


Abstract
As 2020 begins, the natural rubber (NR) market could begin the year witnessing strong supply limitations. The major rubber-producing nations such as Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand have been grappling with a fungal disease known as Pestalotiopsis disease, which has affected hectares of rubber plantations as of Q4 2019. According to the ITRC, because of the outbreak of the disease, production from member countries could be reduced by 800 KT.
One of the major factors contributing to the disease is the use of low-cost fertilizers that were bought by farmers and plantation owners during times of low prices. The major concerns prevailing in the market is that the damage associated with the disease can stop ongoing tapping practices and can impact the plantations’ overall health, leading plantations owners and farmers to abandon the planted trees as well.
Even though its impact is felt largely at the supplier side, the ongoing weak demand from key downstream sectors such as automobiles and tires did not have enough impact to raise price sentiments. However, as 2020 begins, the market will face further reductions in supply from the impact of the annual Southwest monsoon (November to December) as well as the onset of wintering season (February to May).
If the pent-up demand witnesses a rebound in H1 2020, then market and price sentiments would rise to high levels. Even when peak production begins in October 2020, market participants are worried that the ongoing spread of the fungal disease and its lasting impact on existing plantations may not support the onset of the tapping process for the year.
This article examines the following points:
|
Key points |
|
Market performance in 2019
The NR market has been on a downward trend in terms of demand and price sentiments. With continuous escalations from the U.S.–China trade war and the stark decline in demand sentiments from the automotive and tire sector, weak consumption trends with economic and manufacturing slowdowns were some of the major factors that influenced these weak market sentiments.
The advent of stricter environmental regulations toward automobile production, weak manufacturing trends, and a combination of economic and political uncertainties have hampered the buying trend for NR as a raw material. This has been combined with a wait-and-see approach adopted by buyers and tariffed downstream products; the continuous trade escalations also affected market movement.
For example, in the key consumption region for NR, total vehicle sales in China dropped by ~11 percent from Jan.–August 2019 Y-o-Y compared to the same period the year before. From the latex goods sector, the U.S. had imposed a 15 percent tariff (phase 1) plus a 25 percent tariff (phase 2) on medical gloves from China, leading to weaker export sales.
However, as H2 2019 progressed, supply limitations were observed in the market that affected the onset of the tapping process in the traditional peak production season beginning in October 2019. Since demand and buying momentum were low, this did not generate enough pressure to raise the prices.
The onset of supply limitations
As 2019 progressed, supply trends were constrained, beginning with the ITRC export scheme in April 2019 (and lasting for four months), which was a decision made to increase domestic price offers and get rid of excess stocks. The scheme was implemented during the wintering season, during which the leaves shed and market participants tend to halt the tapping process, making it a lean supply period. The first half of the year also witnessed incidents such as a delayed but heavy monsoon season, lashing the plantations and impacting the tapping process before the arrival of peak production.
Traditionally, the market moves to a lean production period from February to May, which is then followed by a period of monsoons in India and Indonesia and light-to-medium monsoons for Thailand and Malaysia.
Thailand and Malaysia further experience the onset of the Southwest monsoon as Q4 ends. October sets the tone for the peak production season, which indicates the supply levels for the year.
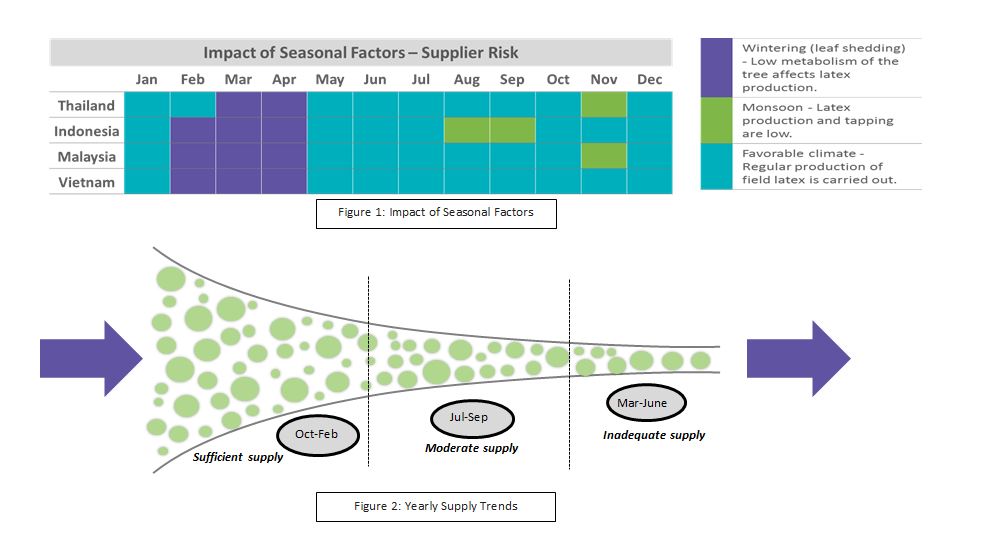
The three major NR-producing nations, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, control 70 percent of the global production levels. During the ITRC export scheme, these nations lowered exports by 441,648 tons, which exceeded the target cutoff of 240,000 tons. However, the export demand was marred by weak consumption trends during the peak export manufacturing season and by trade escalations, leading to a decline of 500,000 tons (January–August 2019) in exports, compared to the previous year.
Onset of the fungal disease Pestalotiopsis across all the key production bases
Pestalotiopsis was first witnessed across multiple plantations in Indonesia, including North and South Sumatra, Bangka Belitung, South Kalimantan, Central Kalimantan, and West Kalimantan. Furthermore, weather and climatic patterns spread the disease onto plantations in Malaysia and Thailand as well.
As of Q4 2019, this fungal disease has affected around 382,000 hectares of rubber plantations in Indonesia. At least 50,000 hectares of plantations in Thailand and 5,000 hectares in Malaysia have been affected as well. One of the major factors contributing to the diseases is the use of low-cost fertilizers that were bought by farmers and plantation owners during times of low prices. According to market participants and rubber organizations, as 2019 ends, 800,000 tons of rubber output could be affected. This would not only impact the domestic production sentiments, but also export trends. For example, in Indonesia alone, the rubber association Gapkindo estimates a drop of up to 540,000 tons in exports this year due to the disease alone.
Market performance in 2020
As 2020 progresses, the supply limitations are unlikely to ease, as the plantations that have been affected by the disease will find it difficult to do continuous tapping, leading to a further decline in output. As the winter season begins, the trees that remain unaffected by the disease will shed their leaves, adding pressure to the supply limitations, especially from February to May, followed by the isolated monsoon season.
Until the beginning of Q4 2019, since the demand from downstream tire and auto sectors was quite low, with weak buying momentum due to the U.S.–China trade war, the prices had not increased sharply.
However, with the possibility of a trade deal between U.S.–China that may ease on consumer products, footwear etc., beginning in mid-December, the buying momentum could witness a rebound along with restocking activities ahead of winter season as well. Hence, prices are likely to be impacted more strongly as 2020 progresses. Typically, prices tend to drop from October to November, beginning with the onset of peak production season. However, the market participants are concerned that the disease could have a stronger impact and may delay production for 2020.
For example, SMR 20 rubber from Malaysia is likely to witness close to a 4–6 percent price hike in December 2019 when compared to November 2019. Moreover, the trend can further expect increases as 2020 progresses; SMR 20 prices could increase by 7–9 percent, strongly supported by supply limitations, even with modest to soft increases in downstream demand.
How buyers can avoid supply risk and establish supply assurance for 2020 volume contracts
Price risk: Supply constraints would likely be the most impactful factor as H1 2020 progresses, which would be a combination of the damages from the fungal disease, the onset of peak winter season beginning in February, as well as another possible export curb scheme from the ITRC. Market participants are yet to finalize the volume of affected supply that would be carried into 2020. With this on track, NR prices are likely to witness possible increases of 6–7 percent as a yearly average across all three key regions. Hence, Q1 to Q2 and the end of Q3 are likely to remain as high-priced quarters with high price-risk volatility.
Supply assurance: Traditionally, efficient NR sourcing is favorable from October to February, when prices tend to remain stable-to-firm, while supply assurance is high in line with the peak production season. However, with the current market events, supply assurance would be low until the wintering season and export scheme ends, which will dig into tapped output and inventories as well.
Sourcing practices for buyers: To avoid the high impact of supply risks, NR buyers can either lock in contracts for 2020 with December price indices before the price increases further, or avoid supply risks with current output and inventories. In H1 2020, buyers can wait until the February price indices, as during this month, the sentiments from Lunar New Year holidays will lead to market participants retreating away from trading activities, accompanied by waning demand and low prices as well.
Currently, this disease is widespread in key Southeast Asian countries; alternately, buyers can investigate other key regions such as Vietnam (within Asia) and the Ivory Coast. Due to increased acreage and investment, Vietnam now has risen to become one of the top exporters of NR. This could be considered an upcoming destination source apart from Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia, etc. Outside of Asia, the Ivory Coast is also a top exporting country in Africa and can serve as an alternate source of procurement.
References
- Market News, Suppliers Websites, several articles
- Beroe Database
- Expert Insights
- Trading Economics, ANRPC, Global Rubber Market News
- Figures 1 & 2: Beroe sources
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe






