
Fostering the Translation Process by AI-powered Machine Translation Services


In the digital era, companies are more focused on automation and optimization to attain value. Most organizations are using different combinations of technologies to achieve a smooth translation workflow. There are diverse translation technologies to improve process efficiency, manage high volume content, ensure quality and consistency, reduce costs, and achieve a faster turnaround time. Technology tools such as Translation Management System (TMS) platforms (process automation), Translation Memory (TM) tools, Computer Assisted Translation (CAT), and Machine translation (MT) are extensively used. However, most companies are still in a conundrum when it comes to procuring post-MT editing services (MPTES). Achieving high quality and accurate output is essential, as the cost involved in MTPES depends on the quality of MT output. Advanced machine translation techniques such as AI-powered MT is a prominent solution to manage large volumes of content, with high accuracy rates.
As global markets and businesses expand, demand for Translation technologies is increasing. Corporations often translate large volumes of technical, product, and marketing content that can be complicated, technically specific, and include essential/critical or confidential company information.
Key challenging factors while translating large volumes of content are content complexity, time to market, quality, and cost. Addressing all these factors is essential for an organization. As technology progresses, few companies are integrating advanced Machine Translation solutions to manage translation performance and spend.
Machine Translation (MT): MT is a statistically automated translation method to translate the content (both verbal and written) from source to target language. Different MT models/methods have evolved. Neural MT (NMT) is currently a widely adopted method; however, AI-powered machine translation is an emerging trend in the developed markets. Most organizations in the Pharmaceutical, Healthcare, and Manufacturing industries are using AI-powered MT services to attain high-quality output.
|
Rule-Based Machine Translation (1970) |
Statistical Machine Translation (2002) |
Neural Machine Translation (2014) |
AI-Powered Machine (2017) |
|
|
|
|
AI-powered Machine Translation
AI-powered MT (AI-MT) comprises a well-trained MT engine with deep learning and neural networking data derived from the corpora/data repositories of businesses. The platform is integrated with the IT infrastructures of businesses. The integrated platform allows clients to create segments/profiles by enabling the business user to add domain-specific training and terminology data. The AI-MT tools can support more than 800+ language combinations with different file formats such as PowerPoint, Excel, Word, Web content etc., without altering their formats.
Pros
-
Domain-specific MT engines to support secure translation without any data leaks.
-
Exponentially faster than human translation. Able to generate thousands of words each minute
-
A human translator can translate around 2,000 words a day.
-
Handles a large volume of content
-
Cost-Effective
-
Increased productivity
Cons
-
AI-MT’s level of accuracy is expected to be 85 – 90%.
-
Accuracy is not consistent.
-
MT does not support certain file types for translation, e.g., jpeg, graphical representation.
-
Creative, cultural aspects of the content may not be correctly handled.
Machine translation Post Editing Services (MTPES)
-
Though MT is quick and cost-effective, content cannot be directly used, as 100% accuracy is not assured through MT. Hence, skilled human translators play a key role in bridging the quality gaps in Automatic translation output.
-
A Machine-translated, significantly high-volume content may contain some errors, and manual corrections are a must.
-
There are two types of MTPES
- Full editing services (50 percent of the translation rate is charged for full editing)
- Light-editing services (20–30 percent of the translation rate)
Trends in Translation Management:
-
Globally, multinational companies are emphasizing localization. Quality is crucial in localization. Buyers are focusing on streamlining the translation workflow, attaining quality, and managing the translation spend.
-
Currently, cloud-based MT services are gaining importance. Cloud Translation helps to manage projects with better accessibility through a dashboard solution.
-
Most global suppliers offer portal services to clients who opt for a large volume of document translation in multiple languages.
-
Unilever, Pfizer, and Sanofi use integrated, intuitive tools to enhance the translation process experience.
-
Buyers are keener to procure services with advanced features such as:
- Specialized reporting
- Email notifications to alert changes on project status
- Automated terminology capture features
- Ability to track departmental translation expenditures
- Centralized project management (global view)
- Engaging with fully integrated translation technology providers (as observed in North American countries)
- Outsourcing Traits: Companies use centralized hybrid translation to streamline translation activities and achieve process efficiency, spend visibility, and cost-savings.
Centralized Hybrid translation - Most companies are using 80% AI-MT and 20% human intervention in the MTPE stage.
-
Buyers are opting for light editing services (cost-effective compared to full-editing services), as the AI-MT assures 90% accuracy.
-
Technology (TMS)
-
Improved/centralized decision-making capability and spend visibility
-
Improved quality via standardized processes, and achieving cost-efficiency
-
Standardized project management processes
-
Access to centralized assets (TM, glossaries, etc.)
Traditional Translation with a Decentralized Approach - Companies with low spend and fragmented structures at the regional and country-levels are still using traditional human translation services.
-
High quality but time-consuming
-
Expensive compared to MT (high cost for complex languages)
-
No central responsibility for the quality delivered
-
Fragmented and differing processes
-
No sharing of assets and best practices
-
Staggered deliveries and time-to-market
|
Key Implications of Centralization vs. De-centralization |
||
|
Factors |
Centralization |
De-centralization |
|
Quality |
|
|
|
Cost |
|
|
|
Consistency of data |
|
|
|
Accountability |
|
|
|
Transparency |
|
|
|
Risk |
|
|
|
Redundancy |
|
|
Best-in-class organizations’ approaches
Fortune 500 companies are investing in process optimization to achieve increased performance and cost-savings by deploying cloud-based translation tools
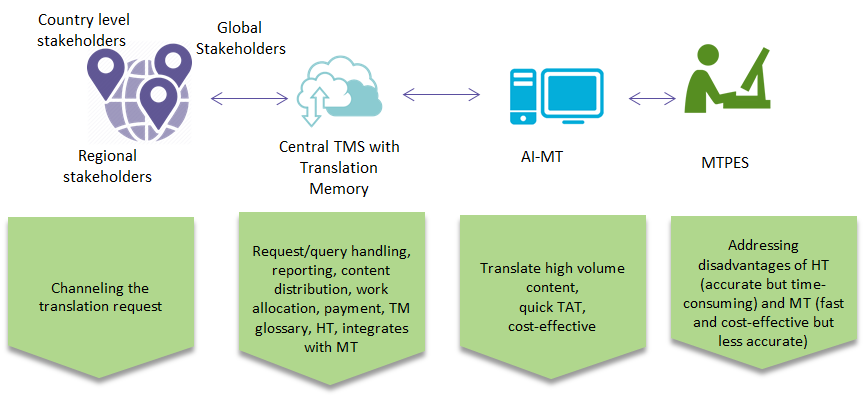
Translation Process Optimization
Conclusion
In most global organizations, localization operations are carried out in a decentralized manner where local and regional procurement teams engage with multiple LSPs for different translation activities. Lack of spend visibility is a challenge. Time invested in administrative work for translation services and supplier management is vast. Opting for both human and machine translation would not provide clarity in reading spend visibility. Integrating the cloud-based advanced AI-MT technology tools would help the organization achieve cost efficiency, quality, and reduced time-to-market. AI-driven machine translation will be a game-changer in corporate translation services. The MT market is driven by the increasing adoption of advanced technologies to simplify language translation across regions, especially in European and APAC regions.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe





















V