
Procurement’s latest test: measuring Innovation’s intangible value

Harish Soundararajan, Associate Principal - Industrial Operations, Maintenance & Site Services, and Sridevi Akkarajuvenkata, Senior Client Partner – Technology

Over the years, procurement has evolved from focusing only on achieving cost savings to becoming a key driver of continuous business growth.
To be sure, cost savings continues to remain an important goal of global procurement organizations. However, as companies chase the game of value addition, new imperatives have emerged out of complex business landscape besides cost savings. Procurement organizations will have to view their role through the prism of Cost, Speed, Flexibility, Innovation and Risk.
Everyone understands the basic concept of Innovation, but the challenge remains as to how procurement organizations can use as well as measure the intangible value generated by Innovation across the supply chain.
With a drop from 2016 in supplier collaboration as a priority from 39 percent to 26 percent and a reduction in the restructuring of existing relationships in favor of increased competition, generating innovation and managing risk will likely become increasingly difficult for procurement, according to Deloitte Global CPO Survey.
Yet it pays to be an innovative company. The 2015 Top 100 Innovators outperformed the MSCI World Index in revenue by 6.01 percent, employment by 4.09 percent, and market-cap-weighted R&D spending by 1.86 percent, according to Thomson Reuters Top 100 Global Innovators report.
Typically, departments such as R&D and Marketing have been earmarked for innovation. The trend is now slowly but surely changing: there is now a growing need to share the ownership of innovation across the business, and interestingly some of the efforts in innovation have been pioneered by procurement organizations.
Gone are the days when procurement was seen only as a tactical function. The function as a whole is now becoming more strategic in nature. For their part, procurement managers are working on various plans to deliver value to their business stakeholders. Important among them is harnessing innovation across the supply chain.
Contrary to what many think, procurement organizations do deal with innovation on a regular basis -- be it evaluating suppliers to purchase new-age drones or connecting business stakeholders with innovations in the marketplace.
Innovation – what does it really mean?
The internal viewpoints on innovation are:
- An initiative that is new to the organization
- Delivers value beyond the contractual cost savings
- Produces value in terms of product improvement
- Process improvement and provides a competitive advantage
Innovation and Procurement
Several procurement organizations have launched a number of innovation initiatives that have resulted in delivering value to business stakeholders.
-
Creation of new role
Some leading companies have created specific profiles such as “innovation manager” within the procurement teams. The procurement innovation managers seek out synergies across categories, and are essentially specialists who work closely with various business functions such as R&D, Marketing and so on. Their role is twofold. On the one hand they translate business strategy to suppliers, and on the other they ensure that what is asked of suppliers is consistent with business priorities.
-
Creation of technology platforms
There are companies who create product or technology platforms within procurement to leverage innovation. When a supplier is approached, the organization does not approach them with only one project or one category that requires development. They approach them by saying: “here is our platform and these are our business challenges across different verticals.” If the supplier manages to find a solution, the potential for the supplier is not only in one business, but in multiple ones. The return on investment for the supplier becomes much higher.
-
Centre of excellence model
The Center of Excellence (CoE) is established within procurement organization to exclusively focus on engaging with internal and external ecosystems. Generally, members are from diverse teams with cross functional experience.
-
Open Innovation Team
Some leading innovation pioneers have a dedicated Open Innovation Team within the R&D team. The procurement innovation managers and R&D work closely at either the category level, or at the leadership level.
Tapping supplier led innovation
There is tremendous emphasis on supplier led innovation. Organizations have enabled procurement organization to own the supplier ecosystem to drive supplier-led innovations. Many organizations also believe that suppliers are the most important source of untapped innovation potential. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) program is essential to harness this route.
Some of the approaches to supplier led innovation are:
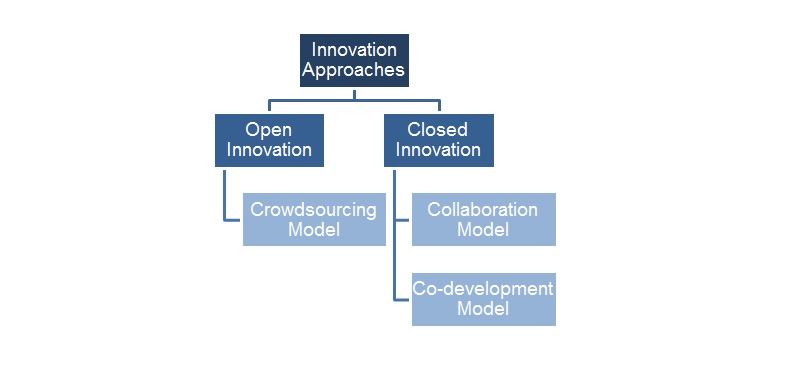
- Crowdsourcing Model: In a crowdsourcing model, organizations invite ideas from different suppliers on a common portal, which in turn are channelized through subject matter experts for validation and feasibility analysis. Most effective ideas are taken into further business plan.
- Collaboration Model: In a collaboration model, organizations work with multiple suppliers simultaneously towards an innovative solution
- Co-development Model: Joint Business Plans with a specific supplier to come up with an innovative solution -- either a product or process innovation.
|
Innovation Model |
Preferred capabilities |
|
Crowdsourcing Model |
|
|
Collaboration Model |
|
|
Co-development Model |
|
- Transparency in the process: Organizations must maintain transparency in the SRM program with both internal stakeholders and external suppliers. The transparency in the system can act as a feedback mechanism between external suppliers and internal business units, and wins the trust of the suppliers. Benefit-sharing between the organization and the supplier, including non-financial benefits, must be clearly stated. For example, sharing patent rights while developing an innovative product.
How do we measure innovation?
Organizations though keen on innovation, are yet to develop robust systems to assess innovation that brings about intangible value.
• Synapse Committee
This ties into one of the roles of the procurement innovation managers. The innovation managers collect ideas and put together (in each of the categories) a so-called Synapse Committee composed of decision-makers from the respective category, such as marketing innovation director, R&D director, consumer insights director and assign some resources to explore promising ideas further.
-
Linking metrics to the outcome
Outcomes must have a specific measurable performance indicator that is meaningful and important to a business stakeholder. Each supplier relationship is developed with a specific business outcome in mind. Outcomes must have a specific measurable performance indicator that is meaningful and important to a business stakeholder. Business outcomes drive the relationship process, the course of action, and level of investment through initiation of projects focused on achieving the outcome.
Procurement organizations must include new KPIs for supplier innovation in the SRM process which would measure the current performance of the suppliers and guide the suppliers to be innovative.
|
Innovation focused KPIs |
|
|
Overall Project Value |
Supplier Involvement |
|
|
CONCLUSION
It is important for procurement organizations to figure out a process to measure innovation as they have the potential to become an effective conduit for flow of ideas between suppliers/marketplace and business stakeholders. Moreover, since procurement teams bring supplier innovation into the organization, any idea acquisition process needs to be integrated into a robust SRM program. Also, there has to be an innovation assessment process as well as a procedure to protect intellectual property rights. Innovation brings about intangible benefits -- the key lies in measuring those benefits through a systematic process.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe







