
Global Economy Demonstrates Resilience Amidst Divergent Recovery Paths


The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has unveiled a report that underscores the unexpected resilience of the global economy, which, despite facing several adversities such as the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and inflationary pressures, continues to exhibit slow and uneven growth rather than stalling, with notable divergences across different regions.
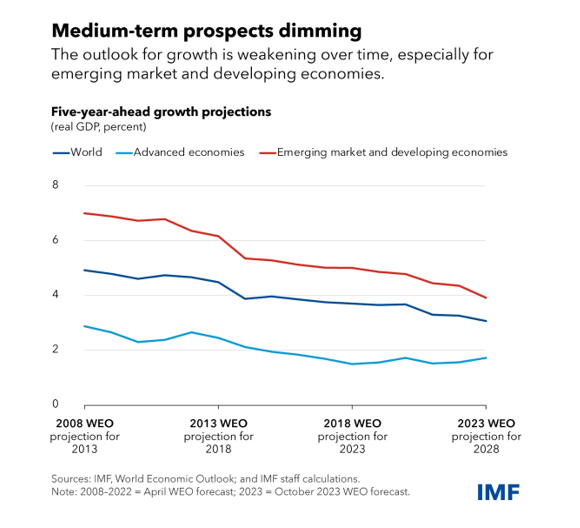
The IMF's analysis points out that the global economy, while not sprinting, is certainly "limping along." This resilience is remarkable considering the disruptions caused by factors such as war-disrupted energy and food markets and significant monetary tightening to combat inflation. However, the growth remains slow and uneven, with projections indicating a deceleration from 3.5 percent in 2022 to 3 percent in 2023 and a slight dip to 2.9 percent in 2024. This slowdown is significantly below historical norms and comes with a backdrop of headline inflation expected to decrease from 9.2 percent in 2022 to 5.9 percent in 2023 and 4.8 percent in 2024.
One key insight from the report is the increasing likelihood of a "soft landing" scenario. This involves a reduction in inflation without triggering a significant downturn in economic activities. This scenario seems increasingly probable, especially in the U.S., where the forecast for unemployment shows a modest increase from 3.6 percent to 3.9 percent by 2025, according to IMF.
However, the recovery is not uniform across the board. The report highlights significant divergences, with some regions experiencing a much slower recovery than others. Advanced economies are seeing a more pronounced slowdown compared to emerging markets and developing countries. The U.S. growth outlook, for instance, has been revised upwards due to resilient consumption and investment, while the Euro area faces downward revisions. Many emerging market economies have shown unexpected resilience, but China is an exception, grappling with a real estate crisis and weakening confidence.
The IMF identifies three critical forces at play in the current global economic landscape:
-
The recovery in services is almost complete, but the strong demand that supported services-oriented economies is now softening.
-
Tighter credit conditions are impacting housing markets, investment, and overall economic activity. This effect is more pronounced in countries with a higher share of adjustable-rate mortgages or where households are less willing or able to use their savings.
-
The aftermath of last year’s commodity price shock continues to influence inflation and economic activity. Economies heavily reliant on Russian energy imports experienced a steeper increase in energy prices and a sharper slowdown.
Despite these challenges, labor markets in advanced economies remain buoyant, with historically low unemployment rates. Real wages are catching up, but there's little evidence of a wage-price spiral.
However, the IMF cautions against several risks on the horizon. China's real estate crisis could worsen, commodity prices could become more volatile amid climate and geopolitical shocks, and inflation, while decreasing, remains high. The report also points out that fiscal buffers have eroded in many countries, leaving them more vulnerable to crises.
In terms of policy priorities, the IMF advocates for a continued tight stance by central banks to ensure inflation continues to recede. Fiscal policy needs to rebuild buffers while still protecting the vulnerable, and there's a need for a renewed focus on managing fiscal risks. The report also emphasizes the importance of structural reforms and multilateral cooperation to enhance growth outcomes and prevent geoeconomic fragmentation.
Beroe View
In light of these complex economic dynamics, the implications for the Procurement function globally are multifaceted. The report's indication of slowing growth, coupled with high inflation, suggests that procurement professionals may face continued pressure on supply chains, with increased costs and potential scarcity of materials and goods. This environment underscores the necessity for strategic sourcing, cost efficiency, and risk management practices within procurement to navigate volatile commodity prices and potential supply disruptions.
Furthermore, the divergences in economic recovery between regions imply that global procurement strategies may need recalibration. Sourcing decisions may need to account for regional economic stability, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical risks, especially in industries heavily reliant on global supply chains. The ongoing challenges in China's real estate sector, for instance, could have ripple effects on related industries and global procurement strategies.
Additionally, the IMF's emphasis on the importance of structural reforms and multilateral cooperation signals a need for procurement to align with broader organizational and global sustainability goals. This alignment involves supporting responsible sourcing practices, contributing to supply chain resilience, and participating in corporate social responsibility initiatives.
In this uncertain economic landscape, procurement functions are not just operational; they are strategic assets in contributing to organizational agility and resilience. Procurement professionals must stay abreast of global economic trends, adapting and strategizing accordingly to mitigate risks and leverage opportunities presented by the current economic climate.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe






