Introduction
The persistent rise and unpredictability of fuel prices has emerged as one of the most significant challenges for organizations with high exposure to diesel and gasoline. Fuel costs often represent a major portion of operating expenses, sometimes accounting for up to half of overall costs, making even modest price swings impactful on profitability, budgets, and service pricing.
Economic, geopolitical, and environmental disruptions now translate almost instantly into heightened budget uncertainty, supply chain inefficiencies, and increased freight rates across all modes of transport. For many energy-intensive sectors, this volatility not only impacts day-to-day cost planning but also triggers downstream effects such as shifting contract terms, renegotiation cycles, and the need for advanced inventory strategies.
In this environment, traditional procurement approaches often prove inadequate, prompting firms to seek innovative strategies that blend market intelligence, predictive commodity analytics, and risk management tools. By combining historical data with real-time market signals and predictive models, organizations can move from reactive fuel purchasing to proactive risk management.
A robust, analytics-driven procurement strategy is no longer optional; it is a vital pillar for business continuity, competitive positioning, and profit resilience in the face of external shocks.
Factors responsible for fuel price volatility
Fuel price volatility is shaped by a combination of interconnected economic, geopolitical, and environmental factors:
- Economically, changes in global crude oil supply and demand, refining costs, exchange rate fluctuations, and evolving tax regimes directly influence fuel prices, with downturns or surges impacting operational expenses and industry profitability.
- Geopolitical risks: Including regional conflicts, OPEC+ production decisions, trade tensions, and international sanctions, can quickly disrupt supply chains and trigger sharp price swings, forcing operators to confront sudden budget uncertainties.
- Environmental and seasonal dynamics also play a crucial role: hurricane seasons in major refining centers, cold winter periods that spike heating oil demand, and the transition to cleaner fuels or biofuel blending mandates all create episodic costs and availability issues across global markets.
For instance, the volatility seen during the 2008 global financial crisis caused diesel prices to spike to record highs, followed by steep declines that wreaked havoc on budgeting and freight rates. Similarly, recent years have witnessed pandemic-induced refinery closures, the Russia-Ukraine war, and most recently the U.S.-led incursion into Venezuela, further underscoring the multifaceted nature of disruption in the sector. These dynamics reinforce the need for predictive commodity analytics that can detect emerging risks early and quantify potential impacts. [1] [2] [3]
Operational and financial risks
Fuel price volatility imposes direct and far-reaching operational and financial risks on logistics and transportation providers, placing persistent pressure on already thin profit margins. As diesel and gasoline costs can constitute up to 50% of a road freight operator’s expenses, even moderate price swings create significant fluctuations in overall operating margins and often force companies to increase shipping rates, pass on surcharges, or absorb losses. Budget planning becomes increasingly difficult in this environment, with unpredictable costs undermining the accuracy of financial forecasts and complicating resource allocation for fleet maintenance, infrastructure, and growth investments. [4] [1]
Long-term supply agreements face heightened contractual risks, as fuel price escalation clauses and frequent renegotiations introduce tension between buyers and sellers and threaten the stability of supply relationships. Disruptions caused by fuel cost unpredictability have even contributed to the insolvency of some smaller third-party logistics firms. Working capital and cash flow management are also put under strain as companies must maintain higher reserves to buffer against price shocks, while delayed cost recovery and increased inventory costs ripple through the supply chain.
Ultimately, unmanaged fuel volatility erodes bottom lines, disrupts service commitments, and risks the sustainability of logistics operations, representing considerable financial risk. [5]
Smart procurement in volatile markets
Fuel procurement strategies are evolving beyond static, price-focused models toward risk-aware, analytics-driven approaches.
Key elements include:
- Strategic Sourcing and Market Intelligence: Strategic sourcing approaches involve continual assessment of supplier reliability and price benchmarks, allowing logistics businesses to shift purchases across geographies, consider alternative energy blends, and leverage market intelligence tools for real-time price optimization.
- Flexible Supply Agreements and Adaptive Pricing: Flexibility within supply agreements is increasingly vital. Contracts now commonly incorporate escalation clauses and adaptive pricing formulas that adjust with reference to market indices, ensuring equitable cost distribution when prices spike or drop.
- Innovative Contract Structures and Risk Management: Innovations such as index-linked contracts and the strategic balance between spot market purchases and term agreements further insulate operators from unexpected surges while preserving the ability to capitalize on favorable price movements. These adaptable structures not only enable more resilient budgeting but also simplify contract renegotiations and promote lasting supplier partnerships through transparent risk-sharing mechanisms.
Altogether, these progressive procurement tactics empower logistics and transportation firms to navigate complex price environments, ensuring operational continuity and cost predictability while sustaining competitive advantage in volatile global energy markets. [6] [7] Commodity analytics platforms support these strategies by consolidating market data, price indices, and risk signals in real-time – turning them into actionable insights for procurement teams.
Fuel hedging strategies
Fuel hedging is a strategic approach used by companies, particularly those with significant fuel consumption like logistics and transportation firms, to manage the risks associated with volatile fuel prices. In commodity markets, hedging involves using financial instruments to lock in fuel costs or offset potential price increases, thereby stabilizing budgets and protecting profit margins.
- Hedging Instruments for Fuel Risk Management: Common hedging instruments include futures contracts, which allow companies to agree on a fixed price for future fuel delivery, thus providing cost certainty over a specified period. Options strategies enable companies to purchase the right, but not the obligation, to buy fuel at a predetermined price, offering protection while allowing benefit from falling prices, although this comes at the cost of premiums. Swaps and other derivative structures serve as flexible cash flow management tools that can mimic the effects of futures while aligning more closely with physical fuel consumption patterns.
- Blended Hedging Strategies and Trade-offs: Blended hedging approaches involve partial hedges, allowing firms to balance exposure reduction with operational flexibility by hedging only a portion of their fuel needs, thus mitigating risk without locking in prices entirely. Each instrument has advantages and disadvantages. Futures provide price certainty but tie companies to fixed volumes, options offer asymmetric risk protection but require upfront costs, and swaps provide alignment with average market prices but involve counterparty risks.
By integrating these fuel hedging strategies into their procurement plans, logistics and transportation companies can effectively safeguard against price shocks while maintaining the agility necessary for competitive advantage in volatile energy markets. [8] [9] [10] When supported by AI-driven commodity price forecasting, hedging decisions become more precise, improving timing, coverage ratios, and budget outcomes.
Figure 1: Fuel Hedging Strategies

Source: mercatusenergy.com, breakthroughfuel.com
Data-driven decision-making for fuel procurement
Data-driven decision-making is fundamental to modern fuel procurement strategies, where predictive analytics plays a crucial role in anticipating price movements and optimizing purchasing plans.
By analyzing historical fuel price trends alongside volatility indices such as implied volatility and crack spreads, procurement experts can better understand market behavior and forecast potential cost fluctuations. Integration with market intelligence platforms provides real-time access to pricing benchmarks and geopolitical news, further refining decision accuracy and helping procurement managers time their purchases more strategically.
Constructing custom decision dashboards consolidates this diverse data into intuitive visual tools, empowering procurement teams with actionable insights and scenario analyses to balance risk and opportunity effectively. These dashboards facilitate quick responses to shifting market conditions and support transparent communication across the supply chain and finance departments.
Overall, predictive analytics and integrated market intelligence enable logistics and transportation companies to navigate fuel price volatility with greater agility, improving budget stability and procurement resilience in uncertain energy markets. [11] [12] [13]
AI forecasting in commodity risk management
AI-based forecasting models significantly enhance commodity analytics by capturing complex, non-linear relationships that traditional statistical methods often miss. By continuously learning from historical price movements, macroeconomic indicators, refinery utilization rates, inventory levels, and geopolitical signals, AI models can identify early inflection points in diesel and gasoline markets. These models update dynamically as new data becomes available, improving forecast accuracy during periods of heightened volatility. For procurement teams, this translates into earlier risk signals, more informed hedging decisions, and greater confidence in budgeting and contract planning. Rather than relying on static forecasts, AI forecasting enables a forward-looking, adaptive approach to commodity risk management that aligns procurement actions with rapidly changing market conditions.
Advanced risk management models
Advanced risk management models are essential for navigating fuel price volatility, offering organizations robust tools to anticipate and mitigate financial exposure.
Scenario planning and stress testing enable procurement teams to evaluate the impact of extreme fuel price changes on budgets by simulating best-case, worst-case, and most likely outcomes, helping prepare for potential shocks with informed contingency strategies. Monte Carlo simulations, a powerful statistical technique, further enhance this by running thousands of randomized price scenarios to quantify risk exposure and estimate the probability distribution of fuel costs under uncertainty. These simulations allow companies to visualize a spectrum of possible financial outcomes and optimize hedging and procurement decisions accordingly.
Organizations also employ benchmarking and tailored risk tolerance frameworks to define acceptable exposure levels and guide decision-making consistent with corporate risk appetite and operational objectives.
Major logistics providers are using Monte Carlo-based models to stress test fuel budgets and optimize hedging strategies, resulting in more predictable costs and financial resilience during volatile periods. By embedding such advanced risk models within procurement processes, companies gain a strategic advantage through enhanced budget stability, improved risk awareness, and optimized financial performance amid ongoing market uncertainty. [14] [15]
Implementation roadmap for fuel procurement
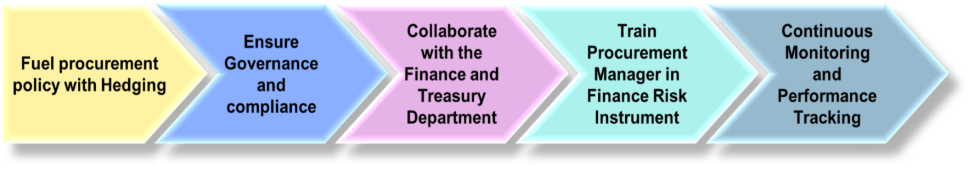
An effective implementation roadmap for procurement teams managing fuel price volatility begins with designing a comprehensive fuel procurement policy that strategically integrates hedging instruments aligned to organizational risk tolerance and operational needs. This policy should define clear objectives, permissible hedging tools, and thresholds for market exposure, providing a structured framework to guide decisions. Governance and compliance considerations follow, ensuring that procurement activities adhere to regulatory requirements, corporate policies, and ethical standards, while establishing oversight mechanisms and documentation protocols.
Collaboration with financial and treasury departments is critical for aligning procurement with broader financial risk management, cash flow planning, and budget forecasting, fostering shared accountability. Equipping procurement managers with training on financial risk instruments, such as futures, options, and swaps, empowers them with the knowledge to execute hedging strategies confidently, interpret market signals, and manage contracts effectively.
Finally, continuous monitoring and performance tracking use real-time data and analytics dashboards to assess hedging effectiveness, budget adherence, and supplier performance, enabling timely adjustments and ongoing learning. This iterative process ensures procurement teams can respond dynamically to evolving market conditions, maintain budget stability, and sustain operational resilience. [16] This structured approach ensures procurement strategies remain adaptive as market conditions evolve. [17] This structured approach ensures procurement strategies remain adaptive as market conditions evolve.
Figure 2: Implementation Roadmap for Fuel Procurement
Source: www.spendedge.com, droppe.com
Conclusion
Diesel and gasoline price volatility presents ongoing challenges, but organizations are not powerless. By integrating commodity analytics, AI-powered forecasting, and structured risk management, procurement teams can improve budget stability, protect margins, and enhance operational resilience.
As fuel markets continue to evolve, shaped by geopolitics, sustainability mandates, and energy transition, predictive commodity intelligence will become an essential capability. Solutions like Beroe’s Commodity Analytics provide organizations with the tools they need to navigate price volatility. By offering data-driven forecasts, scenario analysis, and real-time insights, Beroe empowers procurement teams to manage risks, optimize budgets, and uncover strategic opportunities.
In volatile energy markets, better forecasting is not just an advantage – it is a necessity.
References
[1] T. Cullen, “THE PRICE OF OIL, FUEL,” Ti, Global, 2022. https://www.ti-insight.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/The-price-of-oil-fuel-and-the-impact-on-freight-rates-LB-final.pdf
[2] G. C. D. F. Angelo Martino, “THE IMPACT OF OIL PRICES,” EUropean Parliament, EU, 2009. https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/etudes/join/2009/419084/IPOL-TRAN_ET(2009)419084_EN.pdf
[3] Porter Freight Funding, “Navigating Fuel Price Volatility: A Guide for Trucking Companies,” 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.porterfreightfunding.com/blog/navigating-fuel-price-volatility/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[4] Atlas International, “Atlas International,” 14 02 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.atlasintl.com/blog/the-impact-of-rising-fuel-costs-in-logistics. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[5] GoDesta Australia, “Fuel Price Volatility: Examining the Ripple Effects,” GoDesta, [Online]. Available: https://godesta.com.au/articles/fuel-price-volatility-examining-the-ripple-effects-on-australias-road-freight-operators/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[6]K. I. A.-D. S. A. O. M. A. A. V. I. A. Suleiman Ibrahim Shelash Mohammad, “Impact of Crude Oil Price Volatility on Procurement and,” International Journal of Energy Economics, Vols. -, no. ISSN: 2146-4553, p. 15, 15 02 2025.
[7]UniAir argo, “Strategies to Handle Fuel Price Fluctuations in the Logistics Business,” UniAir argo, 15 02 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.uniaircargo.co.id/blog/ekonomi-dan-bisnis/strategies-to-handle-fuel-price-fluctuations-in-the-logistics-business. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[8] N. Kumbalek, Breakthrough, 12 05 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.breakthroughfuel.com/blog/fuel-hedging-strategies-for-market-stability/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[9] N. Kumbalek, “Three Simple Data-Driven Fuel Hedging Strategies for Market Stability,” Breakthrough, 12 05 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.breakthroughfuel.com/blog/fuel-hedging-strategies-for-market-stability/. [Accessed 23 09 2025].
[10] ”A Beginners Guide to Fuel Hedging with Futures,” Mercatus Energy, 23 04 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.mercatusenergy.com/blog/bid/81549/a-beginners-guide-to-fuel-hedging-futures . [Accessed 2025 09 2025].
[11] “Predictive Analytics in Logistics,” Striim, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.striim.com/blog/predictive-analytics-logistics/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[12] “AI driven fuel procurement streamlines procurement processes,” Gep, 02 12 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.gep.com/blog/strategy/ai-driven-fuel-procurement-streamlines-procurement-processes. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[13] T. Rex, “Solving the Procurement Puzzle with Predictive Analytics,” Insights Personiv, 20 02 2024. [Online]. Available: https://insights.personiv.com/blog-personiv/procurement-predictive-analytics. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[14] “Monte Carlo Analysis: A Powerful Tool for Risk Management,” Riskonnect, 12 03 2025. [Online]. Available: https://riskonnect.com/reporting-analytics/monte-carlo-analysis-a-powerful-tool-for-risk-management/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[15] “Understanding Scenario Analysis and Monte Carlo Simulation for Risk Assessment,” Kotak Securities, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.kotaksecurities.com/stockshaala/financial-calculations-and-excel/understanding-scenario-analysis-and-monte-carlo-simulation-for-risk-analysis/. [Accessed 23 09 2025].
[16] “Strategies for Navigating Price Volatility in Procurement,” 23 09 2024. [Online]. Available: https://droppe.com/blog/article/price-volatility-in-procurement/. [Accessed 23 09 2025].
[17] “Streamlined Logistics: Unlocking Success Through Effective Transportation Procurement,” Spend Edge Smart Procurement, 01 27 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.spendedge.com/transportation-and-logistics/procurement-trends-and-strategies-in-the-transportation-industry/. [Accessed 23 09 2025].
[18] Cannon Logistics Pty Ltd, “Cannon Logistics,” 10 03 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.cannonlogistics.com.au/blog/the-impact-of-rising-fuel-costs-on-transport-logistics/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[19] X2UK, “Fuel Prices: The Silent Threat to Manufacturing and Transport,” X2UK, [Online]. Available: https://x2uk.com/fuel-prices-the-silent-threat-to-manufacturing-and-transport/. [Accessed 22 09 2025].
[20] IEA, “Oil 2025 Analysis and forecast to 2030,” INTERNATIONAL ENERGY AGENCY, Global, 2025.
[21] Research and Markets, “E-Fuels – Global Strategic Business Report,” Research and Markets, 2025.
[22] m. gupta, “Fuel Procurement 2025: Emerging Trends & Predictions,” Fuel Buddy, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.fuelbuddy.in/fuel-procurement-2025-emerging-trends-predictions/. [Accessed 24 09 2025].
[23] “Fuel Price Volatility Risk Management,” Unbrex, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://umbrex.com/resources/industry-analyses/how-to-analyze-an-electricity-generation-company/fuel-price-volatility-risk-management/. [Accessed 24 09 2025].
Author
Related Reading