
U.S. Orange Juice Industry: Not Juicy Enough


Orange juice prices in the U.S. have been witnessing an upsurge in recent years owing to the lowered availability of processing oranges plagued by supply losses due to citrus greening. The pandemic witnessed a boost in demand for citrus products, such as orange juice, owing to the associated health benefits of Vitamin C in oranges and consumer demand for immunity and wellness-boosting beverages. The price increases have been capped by a drop in demand, especially after the pandemic, where high prices are a barrier for the industry, causing consumers to look at other options such as apple juice, non-fruit beverages, and flavored water.
Further supply chain disruption has intensified owing to the impact of the recent Ian Hurricane in Florida, which is threatening supply losses. The overall rising inflation, the upcoming recession in the U.S., and losses due to citrus greening disease attacks have thrown the entire orange juice supply chain into a disarray in one of the leading orange juice-producing markets. Challenges from production and output to logistics and operation have necessitated immediate attention on all stages of the supply chain.
With prices not getting any cheaper, industry players (growers and processors) are likely to invest in more collaborative efforts to revitalize the falling industry, as oranges are a major cash crop and signature in Florida. Orchard rehabilitation, disease management and control, and new farm investments are likely to witness an increase with the goal of reviving the industry and developing a sustainable supply chain.
Overview of the U.S. Orange Juice Industry
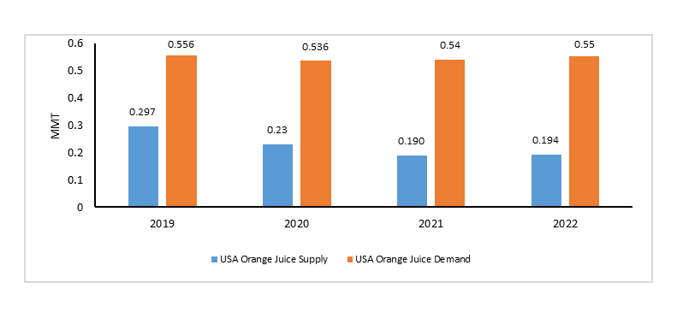
Florida is the leading producer of processing oranges in the U.S., whereas California produces oranges principally for fresh consumption. Orange juice is a traded commodity, and futures prices reflect the overall oranges and juice market. In recent years, the production of Florida oranges has already been poor owing to various parameters, such as contracting acreage due to real estate expansion and citrus greening disease, which have been increasing challenges for growers. Orange juice inventories were at their lowest in five years owing to the impact of supply losses due to citrus greening. The U.S. is moving towards a supply deficit and import-dependent market for orange juice, which would alter the market dynamics globally.
The recent hurricane has caused the greening fungus from abandoned orange farms to be transported by wind to renovated ones, thereby wasting work and investment.
The state budget, effective from July 1st, 2022, included $37 million for the orange and juice industry, with the majority invested in the Department of Citrus marketing programs, research programs, and the Citrus Health Response Program, which includes cultivating new trees resistant to greening.
The overall trend of a slow decline in fruit juice demand globally with growing consumer awareness of health and wellness could also have some long-term impact on juice production patterns with more focus on valorization such as organic, low/no sugar added than conventional juices that are gaining flak for sugar content and additives, among others.
Current Orange Juice Scenario
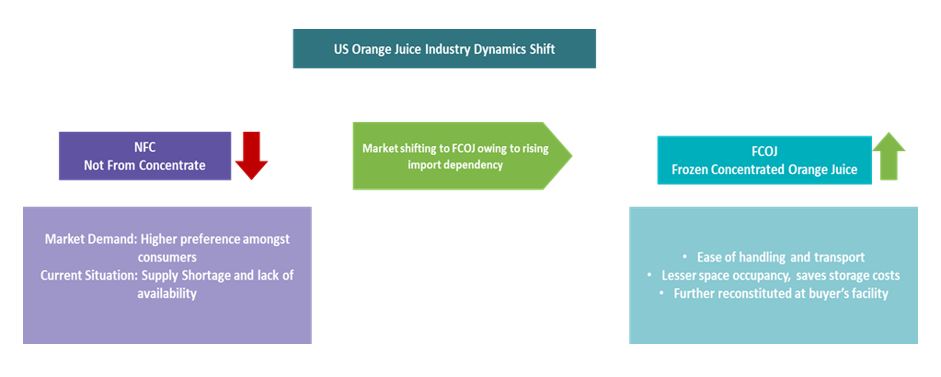
Orange juice futures on ICE exchange are witnessing an uptick of as much as 5.5 percent as of Q3 2022, which is already impacted by citrus greening disease in addition to the recent hurricane Ian in Florida, which is threatening further supply losses. Although imports from other orange juice-producing markets, such as Brazil and Mexico, currently make up most of the orange juice consumed in the U.S., Florida's orange juice sector is critical as it is the major producer of the Not From Concentrate (NFC) variety, which has gained popularity among consumers compared to the older style, frozen concentrated orange juice (FCOJ). FCOJ is preferred by exporters owing to its ease of handling and reduced space occupancy in shipping vessels.
High ocean freights due to port congestion in China and Germany also restrict material movement for global trade, in addition to production challenges. Larger orange juice manufacturers are trying to leverage the empty shelf spaces in supermarkets as other mid-level and smaller players struggle to meet demand.
If the current scenario of low processing oranges availability continues, there will soon be no orange juice coming from Florida, and the market dynamics of Florida will transition from being a leading exporter to becoming dependent on imports.
Industry players: Growers/processors and orange fruit and juice associations are likely to invest heavily in the revival of the orange juice supply chain in the U.S. in the coming years with strategic approaches at all stages of the chain, from seed types to disease management/control of existing orchards; higher fruit yields, acreage, and quality; and sustainable and efficient possibilities for packaging, transport warehousing, and shipping.
Supply Analysis
The 2022/23 orange supply is expected to reduce by at least 8 percent from the previous year, which is also supported by contracting acreage. Growers are using 32000 fewer acres for cultivation, which could be attributable to poor returns, lack of resources, and funds to manage supply losses at orchards, among others. Orange supplies from Florida were the lowest in 55 years in the 2021/22 crop season. The U.S. orange juice output reduced by 17 percent in 2021 owing to a reduction in the availability of oranges for processing. Dwindling inventories for juices will increase the pressure on the current season’s orange output, and this is expected to continue its downtrend.
Orange Juice Supply -U.S.
Demand and Trade Analysis
Shift from Leading Exporter to Importer
The negative health association of sugar in juices; aging populations; nuclear households; less time spent at home during breakfast hours; and competition from other beverage categories such as vitamin water, coffee, tea-based drinks, and other juice flavors continue to be powerful drivers that stress orange juice demand growth, especially in developed markets. However, the overall demand pattern is stable, driven by the regular household table consumption of orange juice, which is the most popular fruit juice category. Re-opening food service sectors, restaurants, workspaces, and educational institutes post the pandemic also support demand strength. Convenient on-the-go small packs of juice are also significant in the convenience beverage sector. Packaged fruit juices have relatively strong demand growth in developing markets.
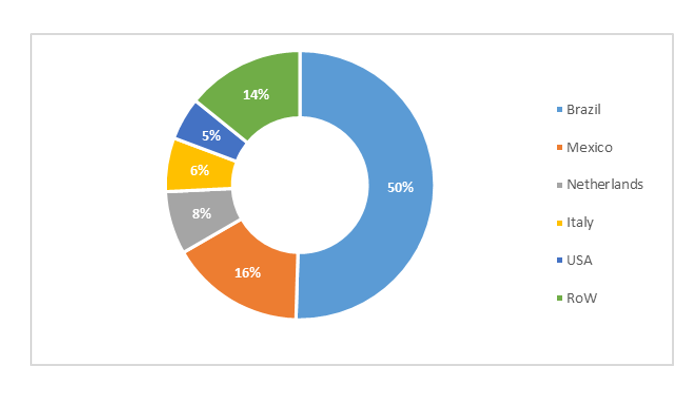
Orange Juice Exports- Global
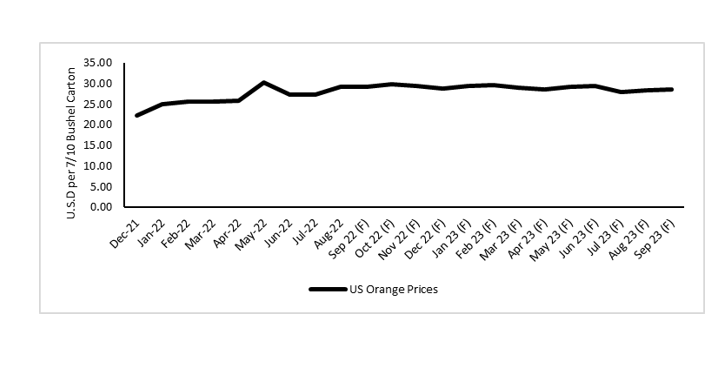
Orange Prices U.S.
Since being the leading exporter after Brazil for orange juice and a self-sufficient market domestically, the dwindling supplies of fruit and juice have led to the U.S. shrinking their exporting power to a mere 5 percent and shifting towards increasing imports, which is a concern for many processors. Juice manufacturers may shift their portfolios to other fruit flavors, such as apples and mixed fruits.
Large suppliers such as Cutrale S.A. decided to suspend shipments of FCOJ products from Brazil to the U.S. owing to high tariffs and surging ocean freights, which have lowered profitability and thereby increased U.S. dependency on Mexico.
The prices are expected to remain bullish, with 2022/23 prices expected to rise by nearly 22 percent, driven by higher imports, which are plagued by surging ocean freights. However, high prices could dampen the demand as consumers may look at alternate choices, mainly apple juice as a replacement for their orange juice, especially in table consumption and convenient for the consumption of juice. The orange juice supply and demand equations were highly elastic. A 10 percent increase in orange juice price could reduce demand by nearly 7.5 percent.
Sourcing Outlook
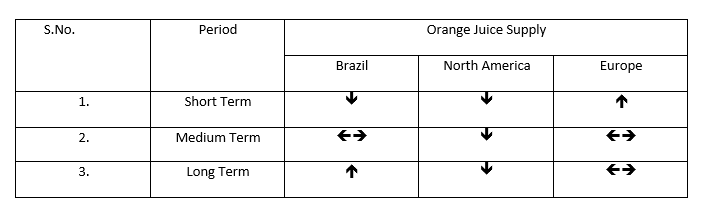
Major FCOJ buyers who were sourcing from the U.S. earlier will look to markets such as Brazil for supplies, which will pressurize the Brazilian market. In addition, the U.S. has also increased its imports from Mexico and Brazil.
For logistical advantages, the U.S. has facilitated Mexican supplies to be almost exclusive to U.S. markets, which would limit Mexico’s potential as a supplier to other markets.
Alternate markets, both existing and emerging markets such as South Africa, Egypt, and Spain, may try to cater to orange and orange juice demand and may have buyers looking to source from these markets.
This will alter the dynamics of the conventional market that has been prevalent for years and bring about new players and supplier bases, which can be considered a major shift.
However, the sustainability and longevity of new players cannot be ascertained for the next few years, especially if the U.S. oranges and juice industry bounces back, which will restore the original supply chain and sourcing dynamics.
The U.S. Orange Juice Industry’s Revival Outlook
Upgrading the supply chain is an avenue for exploration by industry players, who are continuously seeking innovative and sustainable solutions for the revival and development of oranges. Growers, processors, and orange fruit and juice associations could obtain private and government-based aids in reviving the orange juice industry. Many small family-owned farms and ranches may be forced to shut down because they may not be able to remain profitable until citrus greening is curbed.
Research and development have been ongoing intensively since the citrus greening disease started spreading and impacting the industry commercially.
Expanding citrus growing to other states like Texas (a state with similar growing conditions as Florida) is being explored in the U.S. A citrus growing belt that was abandoned after severe frost ions in the 1960s is being reconsidered for revival and orange cultivation. The Citrus Research Board and government partners have announced the California Citrus Research and Field Trials project to reduce the severity of citrus greening and prevent its further spread.
Researchers from the University of Florida are currently testing new methods using artificial intelligence to predict crop yields in citrus groves. Plant breeders at UF/IFAS are exploring new greening-tolerant citrus varieties.
The SAI Platform’s Americas Working Group announced a project for sustainable farming practices in over 90 percent of Florida’s orange industry using the Farm Sustainability Assessment. The project was supported by Cutrale, Treatt, PepsiCo, The Coca Cola Company, Ocean Spray, Florida’s Natural, Symrise, ADM, Florida Citrus Mutual, Peace River Cooperative, Firmenich, and Miritz and is a collaborative initiative between SAI Platform members and local grower groups across all levels of the supply chain. The project aims to improve sustainable on-farm practices such as land use and broader social and environmental best practices.
In 2022, the FDA introduced the Defending Domestic Orange Juice Production Act, which mandates the lowering of the required level of sugar/solids content (brix standard) in not-from-concentrate pasteurized orange juice from 10.5 percent weight of orange juice soluble solids to 10 percent. This act would protect domestic orange growers and the orange juice industry. Oranges did not meet the federal minimum standard of 10.5° Brix, leading industry players to import and blend mandates.
Conclusion
Orange juice is not likely to get any cheaper in the coming year, supported by a significant drop in acreage and supply shortages due to citrus greening and damages due to natural disasters; these could cause some midscale/small level farmers to explore other crop options on their land as they cannot buffer costs and demand drops like bigger growers who are vertically integrated. In addition, the dynamics of the U.S. can change from being a leading exporter to an importer if the situation is not fixed with immediate focus. Many industry players have already begun collaborative approaches with orange growers and processors to revive supply chains. Industry players plan to invest in supply chain rebuilding with a more sustainable approach right from the growing stage to processing up until packaging/warehousing and shipping, which could support the currently falling juice industry in the U.S. The prime focus would be on disease-resistant seed/sapling varieties for new orchards, management of the disease in existing trees, acreage expansions, sustainable packaging, and artificial intelligence-aided logistic support. The orange juice supply chain in the U.S. will undergo major revamp to be functional and profitable for the industry as a whole, which will make this industry dynamic and interesting to monitor in the coming years.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe






