Industry 4.0 adds value to forgings/castings supply chain


Abstract/Business Case
Introduction
Industry 4.0, the latest phase in manufacturing digitization involves a number of innovations that are possible through improved connectivity, data analysis and processing power. In this whitepaper, we study the applicability of Industry 4.0 in the forgings and castings supply chain and the possible benefits and suggestions for implementation strategies.
Main
There are various levels of implementation for making an organization, ‘Industry 4.0 enabled’. These are based on planning, manufacturing execution and machine control. The current scenario in the castings/forgings supply market requires optimization of operational costs and faster reaction to an unpredictable market. These benefits can be attained through industry 4.0 implementation. Cast/forge companies can be supported by the same for improving KPIs such as WIP inventory levels, machine availability, manpower utilization and quality levels.
Recommendation
It is advisable to ensure connectivity and integration at the machine level before proceeding to the planning level. As there are multiple product lines and custom part orders involved, data gathering has to be streamlined before the planning level implementation can be made effective. For the initiative to reach maximum effectiveness, the integration has to be in-sync with vendors so the supply chain can be transformed.
Introduction of Industry 4.0
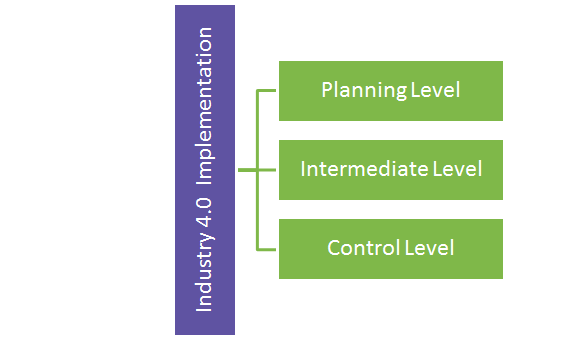
Industry 4.0 refers to the latest phase in digitization of the manufacturing sector. It involves a number of disruptive trends involving contemporary automation, data exchange and manufacturing technologies. The previous digital industrial revolution 3.0 referred to machine control and saw extensive usage of programmable logic controllers. Industry 4.0 can be divided into three levels of implementation:
Planning Level: This refers to overall monitoring of operations and communication at the organizational level. Demand forecasts are tied to production and order placements from vendors to be able to reduce excess inventory levels and react to markets at a faster rate.
Intermediate Level: Also called the manufacturing execution system, this level refers to the job queueing and production floor execution level where focus is on optimization of the production process and equipment predictive and preventive maintenance.
Control Level: This refers to machine control and the flow of material. It is to do with operational parameters such as tracking materials using RFID/bar codes, performing various operations on parts as per varied requirements and ensuring quality in production.
Effect on Castings/Forgings
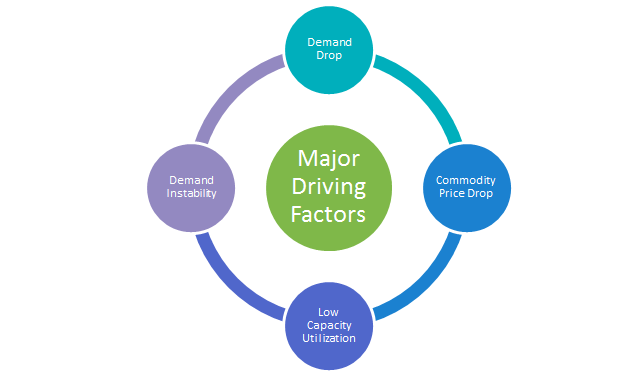
There are a number of factors currently affecting the castings / forgings market. The slowdown in various global economies has greatly pushed down demand and brought in a level of unpredictability into demand forecasting.
The drop in demand globally and especially from the Chinese market has resulted in a number of forge and cast-shops being brought to capacity utilization levels much below their optimum percentages. The current global capacity utilization for forge-shops for example, stands at 60 to 70 percent.
Falling commodity prices have so far helped such shops to stay afloat financially. However, these players too require price cuts for getting volumes to utilize capacities.
In this scenario, operational cost savings help such players to continue operations and ensure a stable supply chain for end-use industries. Industry 4.0, with its advantages and possible savings in terms of reducing skill dependency, optimizing manpower usage, enabling faster reaction-to-market and reducing WIP inventory costs would contribute to providing a platform for market leadership during the current situation.
Industry 4.0 upgrade – An example of a forging company
A global metal forging company with revenues of $2.5 billion recently executed an industry 4.0 initiative.
The organization is a global leader in the metal forming sector. It has a global presence and serves several sectors including automotive, power, oil and gas, construction and mining, locomotive, marine and aerospace.
The company wished to focus on efficiency improvement in their production line and in the business. The aim was to use assembly line data to drive these improvements in efficiency. There were a number of assembly lines available having different machine types, coveyors and robots. A combination of real-time and historical data from the production line was required to be used to achieve end-outcomes.
Some challenges faced included:
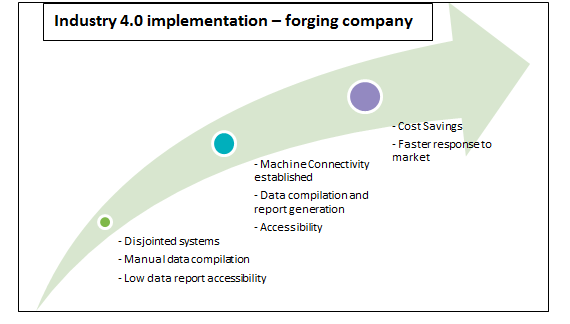
1. Multiple systems individually monitoring different machines in the production line. There was no common data source for obtaining the information
2. A number of machines did not have a monitoring system, for which data was manually compiled resulting in time-consumption and errors
3. The systems of the shop floor were not integrated with the IT system of the organization, making planning reliant on data passed on by manual intervention
4. Data accessibility and mobility of systems was an issue, which was required for effective planning and monitoring of processes
The company then chose an Internet of Things platform from a vendor which was first integrated in the production floor, connecting machines across assembly lines. Data was obtained and compiled to provide insights into the production efficiency and overall equipment effectiveness in the plant.
This allowed real-time visibility into the production in the plant as the platform also integrated with IT systems, providing relevant reports to stakeholders. Energy conservation metrics were also monitored to aid in improving energy efficiency and cutting down on costs. Preventive maintenance and monitoring of machine metrics also helped to cut down on idle time of machines and the production line. Accessibility to systems was improved through integration with mobile and web applications.
These improvements enabled the company to cut down on costs and also respond to changes in customer demands as per the market scenario.
KPI improvements for the Castings / Forgings Industries
Some key performance indicators that can be improved by adopting industry 4.0 related initiatives include:
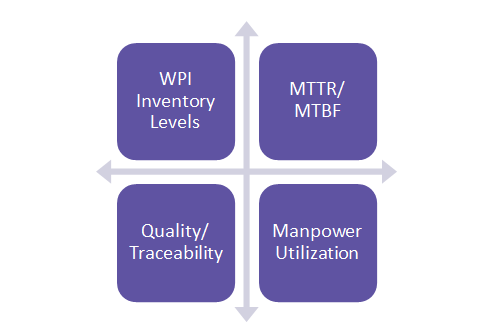
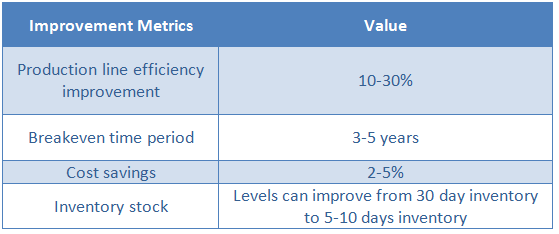
- WIP Inventory: Some major areas of conflict between customized metalworking shops and end-customers are to do with shifting demand projections and changes in part specifications as per requirements. These changes take time to get communicated down the line and result in large amounts of WIP inventory which then is a burden on the metalworking shops and can get passed on to the customer. Digital integration helps prevent the same using seamless communication between stakeholders. A typical improvement for casting/forging shops in this area would be the reduction of 30 days worth of inventory levels to 5 to 10 days.
- Mean time to repair/mean time between failures (MTTR/MTBF): This KPI indicates machine run-time and maintenance which, via proper monitoring that is available via digital integration can be prevented using predictive/preventive maintenance.
- Quality/Traceability: Defect occurences can be drastically reduced since parts would be tagged via RFIDs/barcodes and accordingly slotted into their correct assembly lines, reducing errors and incorrect parts making their way into an assembly.
- Manpower utilization efficiency: With the digital monitoring available and control of machines also integrated in the system, productivity per worker can be greatly improved since human intervention would be required only in certain cases or if there are any breakdowns, greatly saving on labor costs.
Conclusion and Recommendation
The benefits from implementing the industry 4.0 initiatives and digitization far outweigh the costs involved for the forgings and castings markets. This gathers importance in light of the global slowdown and uncertainty in commodity prices and demand forecasting.
According to the industry sources, this is a top-down implementation approach, with OEMs and end-use industries driving the implementation across the supply-chain. The implementation involves vertical and horizontal integration. Vertical integration refers to the type of digitization, whether in planning, intermediate or the control level whereas horizontal integration refers to the links in the supply chain.
Possible improvements that can be seen on such implementation can be defined as below:
It is recommended to proceed with the following approach to implement industry 4.0 for OEMs and forging/casting shops:
1. Control Layer and Intermediate Level: This would apply to the shop floors possessing a higher level of automation so that effective real-time tracking and monitoring can be instituted for the same. The control level is required to be implemented at first to ensure the other layers can build upon this. This would need implementation at the OEM level and along the supply chain for their forge/cast vendors. Implementation here is required before proceeding to the planning level especially given the difficulty in tracking progress of custom-made order progress that exists in this industry and multiple lines of products that would be available on the shop floor.
2. Planning Level: This is required once the first two levels are available to implement progress monitoring and integrate with existing ERP systems to be able to place timely orders with vendors as per real-time requirements. Less time would be invested in conflict resolution with regard to changing demand forecasts and modification of requirements, which is an issue in this industry. Contract clause management assumes much greater significance in this scenario and vendor development and longer-term contracts would be required on implementation.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe