
Consortium Buying Procurement Strategy for Directs & Indirects Categories


Abstract/Business Case
1. Introduction
Consortiums are slowly but steadily establishing themselves as a key strategy in today’s complex supply chains. Purchasing consortiums are quite common in some industries and not quite so in others due to apparent complexities.
2. Main
This paper discusses in detail the concept of Consortium Buying. In this paer we will discuss over topics – pro’s and con’s of consortium buying, its cahallenges, best practices and the various engagement models adopted for consortium buying.
3. Recommendation
The consortium can put forward the “economies of scale” advantage as a type of efficiency. In addition to this, supplier-innovation partnerships can also be considered.
1. Consortium Buying
Adoption of Consortium purchasing is highest in pharmaceutical and healthcare sector. However, adoption of purchasing consortium into other industries is slowly growing. With companies realising increased benefits of group purchasing, adoption is further expected to increase with health care still being the leader in adoption.
Major categories to consider for consortium buying:
- Commodities or raw materials which are not very niche, this may include polymers, agro commodities etc.
- MRO supplier and services
- Facilities services
- IT hardware
- Office supplies and furniture
- Work wear
- Energy Services
Consortium Buying Objectives
1. Drive the prices Downward
Example:
Drive down premium prices like the milk bottle. At one time the HDPE used for making milk bottles was priced at a premium which was a high margin business for the resin producers. But they also provided excellent technical support for the milk producers including how to run the blow molders and build light weighing molds).
The milk producers (bottlers) decided to form a consortium of buyers to gain quantity purchases. With that, they drove the prices down by forcing the resin producers to bid for their business. Ultimately, the milk bottle business became undesirable for many of the resin producers unless they had idle capacity to fill
2. Assure continuous supply
Assure continuous supply to industry for special materials (a growing shortage of LDPE made by the autoclave process used in extrusion coating, solar panels, etc.)
3. Save Money on Bulk Purchase
Save money by gaining bulk volume purchase for lower prices instead of multiple small quantity buys
4. The first move toward integrating backwards and making your own parts
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Above: Pro’s and Con’s of Consortium Buying
Types of Consortium Buying Models
1. Vertical Consortium: Companies those are present in the same industry or market segment
Example:
HealthCare – Veira Medical Group, Provista, Amerinet, Group Purchasing Advantage
Food and Beverage – Foodbuy
Industrial – Prime Advantage
Resin – British Vita
Energy - Gas Intensive
2. Horizontal Consortium: This type of engagement assists companies across different industries
Example:
Indirects - The Purchasing Department, Corporate United
2. Setting up a consortium
1. Find Out Potential Partners
- Set-up a list of potential partners to form a consortium. Small to medium scale buyers will be very interested in this concept especially in Europe where the cost is higher.
- However, big players can also be targeted.
2. Showcase Cost Savings
- Before contacting the potential member review the potential benefits that will be reaped through consortium.
- Big buying power benefits, efficient ordering process as well as strong relationship with suppliers can be showcased.
3. Potential Suppliers
- Compile a list of all the suppliers that the consortium will look at.
- This will be very direct for commodities. However, for indirect categories, the supply base is very diverse.
4. Funding of Group
- Decide on how the group will be funded. It can be administered through a fee paid by the members.
- Set the fee at possible low and bring out the clarity that the fee will be used for operating expense purposes of consortium.
Cost savings is a potential benefit specifically in regions like Europe, which is going under a significant economic decline and unfavourable economics for the petrochemical producers.Streamline processes is another advantage that the consortium buying offers, but, there are potential cost on other verticals such as IT, MRO, Energy, office services etc.
The environment in Europe is conducive for cost savings and consortium buying maybe a probable solution with small to medium players. But, with big guys it might be challenging. Group buying has been more successful in the medical and pharmaceutical industries and has been around for much longer. In recent years, nearly 75% of the total medical and surgical supply was procured through consortiums in the US.
5. Staffing
- Set-up a staffing domain which will take care of the financial account settling, logistics, invoices and services.
- Set-up an office and define job description to staff member. Try to minimize the total cost.
6. Decide on warehousing
- Decide whether the order be shipped to each buyer or at the consortium's office.
- If yes, then select a warehouse space and determine the costs. This can be covered through the feed paid by the buyers.
7.Engagement Models
- Terms and conditions should be clearly written down and clearly mentioned to the each member as well as suppliers.
- A proper agreement should be signed between the consortium and each buyer/seller.
8. Sales Pitch
- Once all things are set-up, make a sales pitch to potential members and make them aware of the potential cost savings that they will attain through consortium.
Key pointers to keep in mind while considering consortium buying
- Check and evaluate the track record of a buying consortium before joining one, also check the focus of consortium in terms of categories they are working into.
- One of the key aspect of engaging with a buying consortium is to assess the existing spend size. Very often with buying consortium, since the contract is negotiated for group of buyers some large companies with huge spend may get overlooked. This problem can be minimized through a total cost of ownership analysis.
- For niche services such as industrial maintenance, choice of consortium is very critical. In such cases a vertical consortium, where in all the participants are from the same industry, helps in getting a best fit supplier, which specializes into delivering services into the target industry.
- While buying through consortium, major buyers often need to assess who other group members are, group buyers with good market reputation, credit line and past reputation may get a better discount when compared to other small buyers. So while selecting and existing consortium or forming a new one it is critical to understand who the members are.
- Lead buyers in a buying consortium may have higher liability, assessing the liability clause in case of failures by member organization becomes important when you have a significant share in overall volume or spend.
- Since a consortium involves number of organisation from different industries, geography and with different management practices, there may at times be difference of opinion. This can be often overcome by having a clear guidelines and rulebook of buying consortium.
Adoption of Consortium Buying
- Adoption of Consortium purchasing is highest in pharmaceutical and healthcare industry. However, adoption of purchasing consortium in other sector is slowly rising. With companies realising increased benefits of group purchasing, adoption is further expected to increase with health care still being the leader in adoption.
- Companies often form an informal consortium to do a joint tendering, this helps in getting the benefits of a buying consortium as well as at the same time administrative burden and liabilities of a consortium can be avoided. Formation of an informal consortium with limited number of companies doing joint tendering is on of the simplest and easiest form of group buying.
- Also Adoption of the GPOs or buying consortium is the highest in USA and still evolving in Europe. Asia is still into its early stages of entering into GPO. This is also because of the geographical complexity of Europe and APAC.
| Industry | Adoption | Growth outlook |
| Pharmaceutical & healthcare | High | Growing |
| Chemicals | Medium | Weak |
| Petrochemicals | Low | Weak |
| Research institutions of universities | High | Growing |
| Automotive | Low | Weak |
| Food & beverages | Low | Weak |
3. Best Practices in Consortium Buying
Forming a dummy Company
- A consortium can be a success only if there is a way to formalise and bring clarity. It is better to form a dummy/bookie company who takes care of the purchasing requirement of the consortium.
- It’s better to sell this concept to the commodity producer this way. Commodity producer can welcome the move, as it can take volume off its competitors while not having to sell its product itself.
Profit Sharing
- The profits can be shared either on (i) Volume basis or (ii) Value Basis
- Ultimately, the reasoning needs to be clearly shared and accepted by the small group of members that are being considered for the consortium.
Engagement Models
- As a model is developed and gradually progress, it is not always the savings on bulk purchase but also the potential savings on soft costs. A lot of creativity goes into establishing an engagement model.
- Initially the engagement can be of short term. Neither side wants to be committed long term as circumstances have a way of changing. Initially a one year contract can be framed with the consortium members and the suppliers which can be renewed afterwards.
Funding of Consortium
- A consortium can be funded by the following ways:
– A fee paid by the suppliers
– A fee paid by the members
– By the combination of both
Most preferred consortium buying strategies
- Consortium buying strategy depends on the type of services required and volumes you have.
- In certain cases, even in consortium buying, it is often recommended that organizations with similar strength and requirements in terms of technical specification should procure together. This may give them higher cost savings. So buying through vertical consortium is often recommended n case of technical services or requirements.
- In case where the requirements are standard, such as office supplies or furniture, horizontal consortiums are good since the possibility of volume consolidation under horizontal consortium are higher.
- Even in a purchasing consortium, lead buyer has greater say into the negotiations. So a clear understanding to the client’s volume can help in understanding their position in the consortium.
- In certain cases, such as facilities services, often joining the volumes from neighbouring organizations or organizations in vicinity through a joint tendering can help in leveraging the volume and this will also offer high degree of customization.
- Buying consortium are generally more successful on national or regional level. Buying through consortiums for global operations may be challenging and may not be rewarding as well. Organizations with significant footprint in a particular region of Europe may leverage such consortiums well.
Benchmarking
- On an average a buying group or consortium can help is realising a cost savings of 10% or up to 15% in certain cases. Majority of this savings is realised from unit cost reduction. Other activities which help is savings realisation includes product standardization, inventory reduction, administrative cost, knowledge sharing etc.
- Average participant company size in a buying consortium is a company with over USD 750 million of turnover and over 5000 employees. Current adoption of consortium buying is around 15%, however same is expected to grow rapidly.
4. Engagement Models
1. Piggy Backing
Characteristics
- An engagement in which smaller firms purchase on the same contracts of larger firms.
- A large firm establishes a contract on its own specification and the same can be used for smaller firms
- Less interaction between group members.
Advantages
- Reduces transaction costs
- Reduces tender time
- Savings could be considerable for small organisations.
Disadvantages
- Not so profitable for larger firms.
- Suppliers do not always allow smaller firms to purchase under the same conditions as of larger firms.
- Organisations cannot influence the supplier choice and there is higher costs involved for parent organisation
2. Lead Buying
Characteristics
- Each member of the group carries out purchasing activity for the suitable products or services according to their expertise or purchasing volume
Advantages
- Similar to third party groups
- Fewer member are required in such organisation
Disadvantages
- Members become highly dependent on the on the expertise of other groups
3. Third Party Group
Characteristics
- Complete outsourcing of purchasing activities to public or private parties. The party establishes contracts to be used by the purchasing members.
- Maybe owned by the member of the purchasing group.
- Less interaction between group members as the interaction is between the member and the third party.
Advantages
- Mainly focuses on economies of scale.
- No high involvement between group members.
Disadvantages
- Members have hardly any control over purchasing organisation.
- Higher number of members.
- Higher number of activities.
4. Project Group
Characteristics
- It is an intensive group for one time purchase, all the member in the group aggregates their volumes and conduct purchasing.
- High interaction between group members as they share knowledge and supply risks.
- This type of purchasing is usually a one-time buy and if successful, the members can work together as a lead buying group or as a program group.
- The organisational structure is simple and members need to consult with one another on specifications as well as suppliers.
Advantages
- Simple organisational structure
- Knowledge sharing which results to more efficiency.
- No steering committee required.
Disadvantages
- Difficult for organisations with less homogeneity.
- Free riding problems
- Members who are actively involved and do more work should be compensated accordingly.
5. Program Group
Characteristics
- Similar to lead buying group but with minor differences.
- Representatives of the member organisations meet and discuss under a steering committee.
- Each member can have influence on suppliers and specifications.
- In lead buying the purchasing activities are often bought by a particular member and hence less control.
- Program groups can have one single contract between the supplier and group or with each member separately.
Advantages
- Sharing of administrative costs.
- Adaptability to each members’ needs.
Disadvantages
- Sharing of confidential information.
- Communication problems
- Allocation of gains and costs due to heterogeneity.
- Higher coordination costs and complexity.
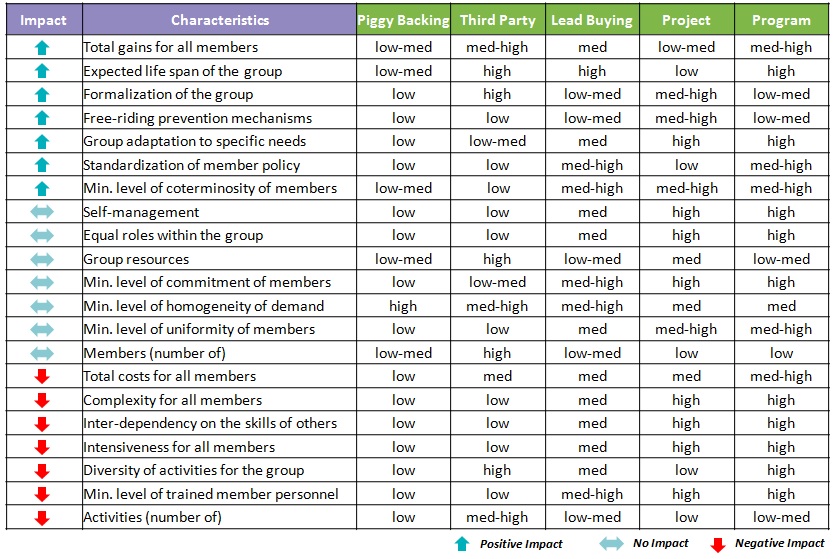
Above: Characteristics of Engagement Models
Summary
The consortium can put forward the “economies of scale” advantage as a type of efficiency. In addition to this, supplier-innovation partnerships can also be considered.
Joint production, purchasing and sales agreement are allowed only if it brings efficiencies to all the undertakings. Small players in the consortium may also strengthen as they will have the ability to compete with the bigger ones.
Fair share of cost savings will be given to the customers in the consortium and since the consortium will consist players from different fields, competition will be eliminated. To be on the safer side, it is advisable to review the legitimacy of the business with the law department.
However, the consortium will be faced with the following challenges:
Competition from Big Buyers: Big buyer’s core area of business might be affected as their margin comes from their volume purchase. Hence, such a strategy might face a challenge from big converters.
Variety in Grades and Supplier Trust: Example - The packaging needs for different companies might be different as there might be a difference in quality standards.
Finding a Prospective Supplier: A supplier cannot jeopardize its relationship with the existing customers and only in case of available excess capacity, can a supplier supply directly to a consortium.
Other Disadvantages: The performance of the consortia depends a lot on individual performances of the members. The liability part of the consortium should be managed properly.
Related Insights:
View All
Get more stories like this
Subscirbe for more news,updates and insights from Beroe






